Demonstrating the evidence-based health benefits of extra virgin olive oil like Morocco Gold
Summary
- In a fast-changing world, it is unusual to re-discover a wisdom of the ancients that is as potent now as it has been for thousands of years.
- It has been known for centuries that high-quality extra virgin olive oil is good for your health and wellbeing. It has also been lauded across many cultures.
- The difference now is that, following extensive scientific research, we know exactly what makes high-quality olive oils so beneficial – their polyphenols and other bioactive compounds.
- Morocco Gold is an exceptionally high-quality extra virgin olive oil from a unique new source. What makes it special is that it is rich in polyphenols, antioxidants that provide protection against a wide range of chronic diseases. This makes Morocco Gold particularly attractive to health-conscious food lovers worldwide.
- Morocco Gold is on a mission to show wellness-conscious food lovers how the simple inclusion of a premium virgin olive oil like Morocco Gold can have a profound impact on health and wellbeing.
Contents
- How Extra Virgin Olive Oil Helps Protect Against Cardio Vascular Diseases
- Polyphenols – Extra Virgin Olive Oils Powerful Antioxidant
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil And The Cardiovascular System
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil And The Digestive System
- How Does Extra Virgin Olive Oil Help The Digestive System?
- How Does Extra Virgin Olive Oil Aid Blood Pressure?
- Extra Virgin Olive oil And Hypertension: Clinical Trials
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil Can Help Fight Inflammatory Diseases
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil: Part Of An Anti-Inflammatory Diet
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil Helps Control Healthy Cholesterol
- The Health Benefits Of Extra Virgin Olive Oil On Cholesterol: A Study
- How Can Extra Virgin Olive Oil Help Improve Blood Sugar Levels?
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil & Diabetes: A Study
- How Does Extra Virgin Olive Oil Help To Keep Bones Healthy?
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil & Bone Fractures: A Study
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil Can Help Combat Osteoarthritis
- Polyphenol Ligstroside-Aglycone (LA) In Extra Virgin Olive Oil : It’s Role In Combating Osteoarthritis
- A Study Of Ligstroside-Aglycone In Treatment Of Osteoarthritis
- Polyphenols In Extra Virgin Olive Oil have Anti- bacterial Properties
- Polyphenols In Extra Virgin Olive Oil Can Help Combat Cancer
- Investigating Polyphenols In Extra Virgin Olive Oil & Their Impact On Cancer
How Extra Virgin Olive Oil Helps Protect Against Cardiovascular Diseases
With growing awareness of the importance of a healthy diet, more people are turning to eating patterns like the Mediterranean diet to help lower cholesterol, reduce blood pressure, support weight control, and improve overall wellbeing. At the heart of these diets is extra virgin olive oil – often called the original superfood.
What makes virgin olive oil stand out is that it has supported human health for centuries. From ancient Rome, where Hippocrates recommended it for over 60 conditions, through to today’s modern medical research, olive oil has always been valued for its therapeutic properties.
Modern studies confirm what history already knew – extra virgin olive oil is one of the most effective natural foods for cardiovascular health. Rich in polyphenols and other nutrients, it helps protect your heart and blood vessels against oxidative damage and inflammation.Choosing our olive oil gives you more than an everyday cooking ingredient. It delivers clinically recognised health benefits while adding unrivalled flavour to your meals. If you want to support
Polyphenols – Extra Virgin Olive Oil’s Powerful Antioxidant
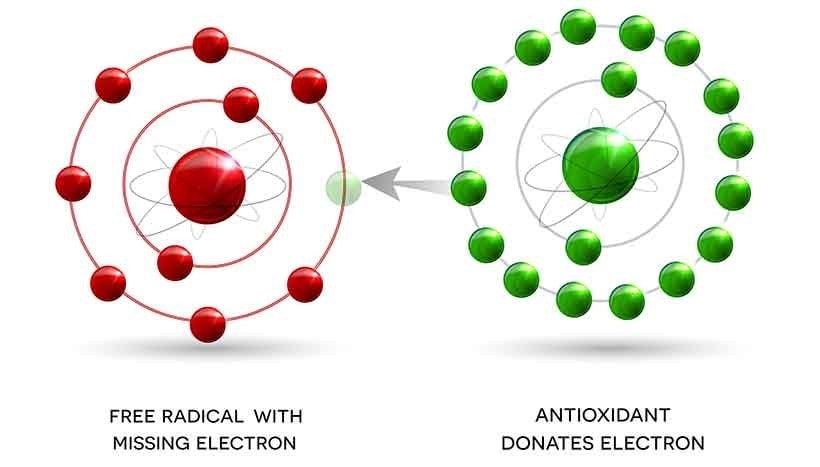
Polyphenols are potent antioxidants that neutralise free radicals and help protect cells from damage. Free radicals are unstable compounds thought to play a role in more than 60 different health conditions, including heart disease and atherosclerosis, as well as ageing.
Several polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil, including hydroxytyrosol, oleuropein, and luteolin, have shown beneficial effects such as avoiding unhealthy blood clotting by keeping blood platelets in check. These properties contribute to the anti inflammatory properties that make olive oil such a powerful ally in protecting long-term health.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil and the Cardiovascular System
Lowering the risk of cardiovascular problems has been the focus of several recent studies on extra virgin olive oil. Chronic inflammation is a risk factor for many types of cardiovascular disease, and olive oil’s well-documented anti inflammatory properties play a central role.
Inflammation in the blood vessels compromises circulation and overall health. Daily intake of extra virgin olive oil – even as little as one tablespoon – reduces inflammatory processes within the blood vessels, lowering the risk of conditions such as atherosclerosis.
Additional health benefits of extra virgin olive oil for the cardiovascular system include:
- Reduced risk of unwanted blood clots
- Lower LDL cholesterol levels and improved lipid profiles
- Better protection of cholesterol from oxidation, reducing damage known as lipid peroxidation
These combined effects contribute to better cardiovascular health and reduced risk factors for heart disease.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil And The Digestive System
“All disease begins in the gut.”
Hippocrates, father of modern medicine
Digestive health problems are common, yet often hidden due to stigma. People with digestive disease may endure pain, fatigue, and constant bowel issues before seeking medical help. Severe cases can result in missed workdays, emergency interventions, and long-term prescriptions.
Including extra virgin olive oil as part of a balanced diet has shown potential health benefits for the digestive system, thanks to its natural anti inflammatory properties and the presence of healthy fats like monounsaturated fatty acids.
How Does Extra Virgin Olive Oil Help the Digestive System?
We all know that extra virgin olive oil is one of the healthiest oil choices for cooking and eating. It is high in fat, but most of it is heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, making it far superior to refined oils like butter or seed oils. Choosing olive oil over less healthy fats supports heart health, helps lower cholesterol, and may also benefit digestion.
As soon as you consume extra virgin olive oil like Morocco Gold, it has positive effects all along the digestive system. Used since ancient times for assorted digestive disorders, its beneficial properties are now supported by scientific research and modern nutritional studies.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil & the Stomach
Eating quickly or consuming high-fat foods can cause gastric reflux or heartburn. A study published in Grasas y Aceites found that extra virgin olive oil may reduce gastric acid secretion. By slowing the release of stomach contents into the duodenum, olive oil helps you feel fuller for longer, aids nutrient absorption, and contributes to better digestion.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil & the Hepatic-Biliary System
One of the most important health benefits of extra virgin olive oil is its effect on bile flow. Olive oil acts as a cholagogue, ensuring optimal bile drainage, and as a cholecystokinetic, stimulating contraction of the gall bladder. This helps prevent bile duct issues and supports the synthesis of bile salts in the liver. By aiding lipid digestion and preventing gallstones, olive oil demonstrates clear potential health benefits for long-term digestive health.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil & the Pancreas
Your pancreas plays a key role in hormone production and enzyme release for digestion. Extra virgin olive oil is particularly beneficial here, as it requires the pancreas to produce fewer enzymes compared with other oils. This reduces strain on the organ and supports long-term function.
The Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health reported that olive oil consumption may even reduce the risk of pancreatic cancer. For patients with pancreatic conditions such as chronic pancreatitis or malabsorption syndromes, virgin olive oil can be an important part of a balanced diet.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil & the Intestines
Replacing less healthy oils with extra virgin olive oil improves intestinal efficiency and enhances absorption of vitamins and minerals. The polyphenols in olive oil, such as oleuropein, hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, and ligstroside, may also help maintain gut health by balancing bacteria and inhibiting harmful strains like Helicobacter pylori, which causes stomach ulcers.
Some polyphenols, including secoiridoids, are under study for their role in reducing cancer risk in the digestive tract. This makes olive oil a powerful component of diets aimed at reduced risk of digestive disease.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil Can Boost Beneficial Gut Bacteria
Looking after gut microbes is essential for digestion and immune defence. Diets rich in plant polyphenols, whole grains, oily fish, and extra virgin olive oil – such as the Mediterranean diet – are associated with higher levels of beneficial, anti-inflammatory bacteria in the gut. This demonstrates the beneficial effects of including olive oil as a core part of your daily meals.
How Does Extra Virgin Olive Oil Aid Blood Pressure?
Polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil have shown the ability to lower blood pressure and support the immune system. Their antioxidant and anti inflammatory properties help reduce reactive oxygen species in the body, lowering inflammation and contributing to overall cardiovascular health.
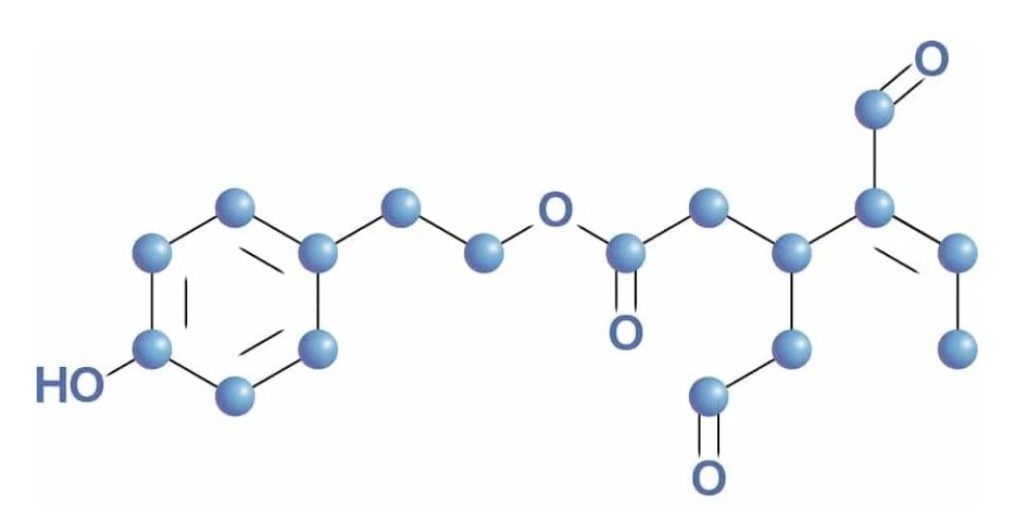
Polyphenol Oleuropein
One of the key polyphenols in Morocco Gold extra virgin olive oil is oleuropein. Studies show it helps prevent LDL cholesterol from oxidising and sticking to arterial walls, reducing a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease. This contributes to the long-term health benefits of including extra virgin olive oil in a heart healthy diet.
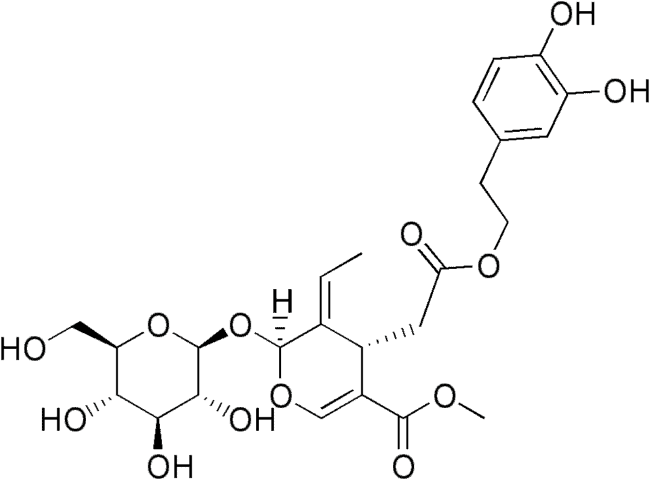
Oleuropein is a natural phenolic compound found in olive leaves and green olives, including the skin and flesh, from which olive oil is derived. It is responsible for the distinctive bitter taste in extra virgin olive oil.
Health Benefits Of Oleuropein
The health benefits of oleuropein include antioxidant and natural anti inflammatory properties, reduced blood glucose levels, and free radical removal. Oleuropein has also been linked to cardioprotective and neuroprotective activity.
Belonging to a group of compounds called secoiridoids, oleuropein has shown activity against bacteria, viruses, fungi, moulds, and even parasites. Studies show that oral intake of oleuropein reduces blood vessel formation, demonstrating strong anti-angiogenic properties. In addition, phenolic compounds in virgin olive oil, such as oleuropein and protocatechuic acid, help protect against LDL oxidation. Extracts from olive leaves and olive fruit containing oleuropein may also protect insulin-producing cells from damage caused by cytokines, helping to reduce insulin resistance.
Extra Virgin Olive oil And Hypertension: Clinical Trials
One of the earliest randomized controlled trials assessing the antihypertensive effect of extra virgin olive oil dates back to the late 1980s. In this study, a diet enriched in olive oil was compared to a low-fat, high-carbohydrate diet in 47 healthy subjects. After 36 days, both systolic and diastolic blood pressure were significantly reduced, suggesting that dietary intake of olive oil could help regulate blood pressure.
Follow-up research confirmed these findings in type 2 diabetic patients, who experienced even stronger antihypertensive effects from a diet enriched with extra virgin olive oil compared to one high in carbohydrates.
Further Studies on Olive Oil and Blood Pressure
While diets high in saturated fat are associated with higher blood pressure, research suggests that monounsaturated fatty acids may have the opposite effect. A study from the University of Naples compared monounsaturated fats from extra virgin olive oil with polyunsaturated fatty acids from sunflower oil in 23 participants.
Participants consuming extra virgin olive oil required fewer antihypertensive medications, with usage cut in half within four months. In contrast, sunflower oil had only mild effects. Cholesterol and triglyceride levels were also slightly lower in the olive oil group. Importantly, olive oil contains about 5 mg of antioxidant polyphenols per 10 g – absent in sunflower oil – which further contributes to its potential health benefits for cardiovascular health and lower blood pressure.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil Can Help Fight Inflammatory Diseases
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection, but when it becomes chronic it can contribute to chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis. Chronic inflammation is also linked to heart disease, obesity, poor sleep quality, and long-term pain.
Because of its unique anti inflammatory properties, extra virgin olive oil can help reduce inflammation and protect against damage caused by oxidative stress. Regular inclusion in a healthy diet lowers the risk of inflammation-mediated conditions and supports overall general health.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil: Part of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
To reduce inflammation, focus on a balanced diet with foods typical of the Mediterranean diet, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, whole grains, oily fish, and extra virgin olive oil. This way of eating delivers long-term health effects, including a reduced risk of chronic diseases and improvements in mood and wellbeing.
Anti-Inflammatory Benefits of Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Phenols and polyphenols are the core substances that give olive oil its anti inflammatory properties. Researchers have shown that even one tablespoon of extra virgin olive oil per day lowers inflammatory signalling molecules such as IL-6 and TNF-alpha.
In Mediterranean countries, daily olive oil consumption has been linked with reduced C-reactive protein (CRP), lower levels of inflammatory enzymes, and decreased oxidative stress markers. Studies suggest that two tablespoons per day of extra virgin olive oil provides strong and consistent anti-inflammatory benefits.
Phenols and polyphenols are the core substances that give olive oil its anti inflammatory properties. Researchers have shown that even one tablespoon of extra virgin olive oil per day lowers inflammatory signalling molecules such as IL-6 and TNF-alpha.
In Mediterranean countries, daily olive oil consumption has been linked with reduced C-reactive protein (CRP), lower levels of inflammatory enzymes, and decreased oxidative stress markers. Studies suggest that two tablespoons per day of extra virgin olive oil provides strong and consistent anti-inflammatory benefits.
The Anti-inflammatory Effect of Polyphenol Oleuropein Aglycone (OA)
Oleuropein aglycone is a glycosylated secoiridoid, a type of bitter phenolic compound found in green olive skin, flesh, seeds, and leaves. The term oleuropein is derived from the botanical name of the olive tree, Olea Europaea.
Oleuropein aglycone is one of the main polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil. It has gained global attention within the scientific and medical communities due to its biological properties, including activity against Alzheimer’s disease, breast cancer, hyperglycaemia, and its strong anti inflammatory properties.
OA is formed through the de-glycosylation of oleuropein during olive maturation and is released during pressing. Studies suggest it helps reduce inflammation by inhibiting COX enzymes, thereby lowering the production of prostanoids, prostaglandins, and thromboxanes — all key contributors to inflammation.
Inflammation is a complex immune response to pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and enables during infection or injury. Pain from inflammation is something most people experience at some point in their lives and a common daily occurrence for many people with arthritis OA plays an anti- inflammatory role during chronic inflammation and improves tissue damage associated with collagen-induced arthritis.
In addition, OA may be responsible for inhibiting cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes. COX is an enzyme that forms prostanoids, prostaglandins, prostacyclins, and thromboxanes, which are all contributors to the inflammatory response. Therefore, OA can play an effective role in anti-inflammatory activities.
Anti-inflammatory Polyphenol Oleocanthal
Oleocanthal, also known as p-HPEA-EDA, is another polyphenol in virgin olive oil. Responsible for the peppery sensation at the back of the throat when tasting fresh oil, oleocanthal has anti inflammatory properties similar to ibuprofen, a commonly used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
This makes extra virgin olive oil a natural source of compounds with pharmacological activity, supporting its reputation as liquid gold in the context of health benefits of extra virgin olive oil.
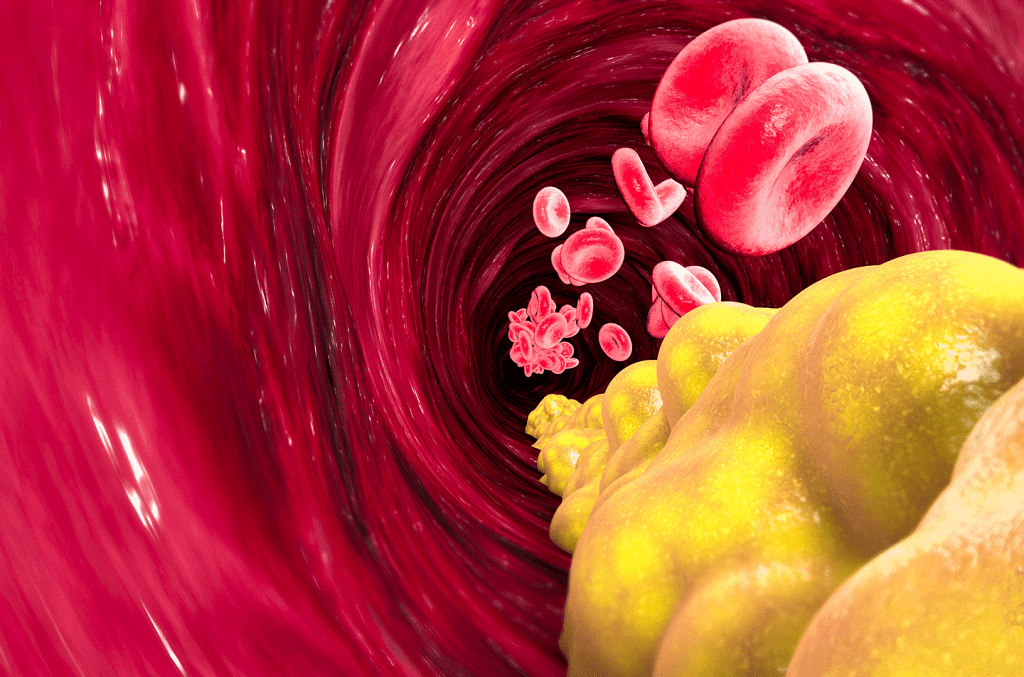
Extra Virgin Olive Oil Helps Control Healthy Cholesterol
High cholesterol occurs when too much fatty substance builds up in the blood. While diet, inactivity, smoking, and alcohol are common causes, it can also run in families. Excess cholesterol can block blood vessels and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and heart disease.
LDL and HDL Cholesterol
Cholesterol travels through the blood on proteins called lipoproteins:
- LDL (low density lipoprotein): “bad” cholesterol. High levels raise your risk of heart disease and stroke.
- HDL (high density lipoprotein): “good” cholesterol. It absorbs cholesterol and carries it back to the liver for removal. High levels reduce your risk.
The Health Benefits of Extra Virgin Olive Oil on Cholesterol: A Study
Research led by Montserrat Fitó, Ph.D., published in the American Heart Association’s Circulation, explored whether a Mediterranean diet enriched with extra virgin olive oil or nuts improved the beneficial effects of HDL.
The study included 296 participants at high risk of heart disease. Three diets were tested over one year:
- Mediterranean diet with ~4 tablespoons of extra virgin olive oil daily.
- Mediterranean diet with nuts.
- A healthful “control” diet with less red meat, processed foods, and high-fat dairy.
Blood tests showed:
- LDL (“bad”) cholesterol decreased only in the control diet group.
- Both Mediterranean diets improved HDL function, with the most pronounced effect in the olive oil group.
Benefits included:
- Improved reverse cholesterol transport (removing cholesterol from arterial plaque).
- Greater antioxidant protection, counteracting LDL oxidation.
- Increased vasodilation, keeping blood vessels open and blood flowing.
Although the control diet contained fruits and vegetables, it reduced HDL’s anti-inflammatory capacity, a negative effect not seen in the Mediterranean diets. This reinforces that a Mediterranean diet enriched with extra virgin olive oil supports cardiovascular health and reduces risk factors for disease.
How Can Extra Virgin Olive Oil Help Improve Blood Sugar Levels?
Tyrosol, a key polyphenol in Morocco Gold extra virgin olive oil, has powerful antioxidant activity. Along with hydroxytyrosol, it is one of the most abundant polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil, contributing to the broad range of health benefits.
Studies show that tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol can protect cells from oxidative injury, scavenge free radicals, and activate the body’s own antioxidant systems. In animal models, these compounds helped reduce blood sugar and support better glycaemic control, showing promise for reducing insulin resistance and lowering the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil & Diabetes: A Study
In a study at Sapienza University in Rome, researchers examined the health benefits of extra virgin olive oil within a traditional Mediterranean diet for people with diabetes.
This small study involved 25 participants who ate a typical Mediterranean lunch of fruits, vegetables, grains, and fish on two occasions. For the first meal, they added 10 g of extra virgin olive oil; for the second, 10 g of corn oil. After each meal, blood sugar levels were tested. The rise in blood glucose was much smaller after the meal with extra virgin olive oil than after the meal with corn oil.
“Lowering blood glucose and cholesterol may be useful to reduce the negative effects of glucose and cholesterol on the cardiovascular system,” said Francesco Violo, lead author.
The findings aligned with previous work linking extra virgin olive oil with higher insulin levels and benefits for people with type 2 diabetes. More surprising were the reduced levels of LDL, or “bad” cholesterol, after the olive oil meal.
The researchers stressed that extra virgin olive oil should be consumed within a balanced diet to see these potential health benefits.
How Does Extra Virgin Olive Oil Help To Keep Bones Healthy?
Adherence to a Mediterranean diet with extra virgin olive oil at its heart was associated with decreased fracture incidence in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition study, involving 188,795 subjects followed for nine years. The Mediterranean diet including extra virgin olive oil was also associated with increased calcium absorption and retention and a decrease in urinary calcium excretion in male adolescents.
Olives and extra virgin olive oil are key components of the Mediterranean diet. A Mediterranean diet enriched with olive oil has been linked with increased markers of bone formation in elderly men.
Mice fed with olive oil showed higher apparent calcium absorption and calcium balance, but lower serum calcium, phosphate, and magnesium compared with groups fed other lipids. This may relate to the high phenolic content of extra virgin olive oil. Phenolic compounds including tyrosol, hydroxytyrosol, and oleuropein exert prominent antioxidant and anti inflammatory properties and are potential candidates for osteoporosis prevention.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil & Bone Fractures: A Study
A recent study followed 870 participants for seven years to see if extra virgin olive oil intake related to fracture numbers. Participants were grouped into thirds by intake:
Lowest third: ~38 g per day (about 3 tablespoons)
Middle third: ~48 g per day
Highest third: ~57 g per day
Those in the highest intake group reported 51% fewer fractures than those in the lowest group. While intakes were high, the results indicate a link between reduced fracture risk and incorporating extra virgin olive oil into an ordinary meal plan. Numerous animal studies also show increased bone formation with extra virgin olive oil, tied specifically to phenols such as tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil Can Help Combat Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a joint condition featuring breakdown and loss of cartilage. It occurs more frequently with age and often affects the hands, feet, spine, and weight-bearing joints such as hips and knees. It can be primary (no known cause) or secondary.
Polyphenol Ligstroside-Aglycone (LA) In Extra Virgin Olive Oil: Its Role In Combating Osteoarthritis
This polyphenol, synonymous with p-HPEA-elenolic acid, is part of the Tyrosol family and has the chemical formula C19H22O7.
Evidence on LA bioactivity is limited, yet it behaves as an antioxidant and shows anti inflammatory properties by down-regulating NF-κB, a factor involved in osteoarthritis and chronic inflammation. LA may also induce a caloric restriction-like state via sirtuins, proteins that help regulate cellular balance.
A Study Of Ligstroside-Aglycone In Treatment Of Osteoarthritis
Researchers at the Faculty of Pharmacy Seville and the Biomedical Research Institute Coruna examined LA and related compounds as anti-inflammatory agents for OA. They tested oleocanthal (OLC), ligstroside aglycone (LA), an acetylated LA (A-LA), and two marine polyunsaturated fatty acids (EPA and DHA).
Results: Acetylated ligstroside showed the most promising effect. It reduced expression of pro-inflammatory genes (iNOS, MMP13, IL1B), lowered nitric oxide levels from cartilage explants, and reduced proteoglycan loss in human osteoarthritic cartilage. These findings support a role for polyphenols in OA therapy.
Polyphenols In Extra Virgin Olive Oil Have Anti-bacterial Properties
Researchers at the National Research Council’s Institute of Food Sciences and the University of Salerno showed that polyphenols from three olive oil varieties inhibited several bacterial strains at low concentrations, confirming broad antibacterial capacity.
All three extracts were effective against Escherichia coli, a cause of urinary tract infections, and against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a pathogen known for biofilm formation. Biofilms are dense microbial communities that can protect pathogens and complicate treatment, especially on medical devices used in surgery.
“These extracts showed notable activity against pathogenic species responsible for biofilms. This could guide complementary studies to formulate natural-origin drugs with optimal polyphenol mixtures for antibacterial efficacy,” said Filomena Nazzaro, senior scientist at the Institute of Food Sciences, Italy.
Polyphenols In Extra Virgin Olive Oil Can Help Combat Cancer
Growing evidence documents anti-cancer health benefits of extra virgin olive oil. Early work used animal or cell models; more recent studies in people including olive oil in daily meals have found encouraging outcomes.
Intakes as low as 1–2 tablespoons per day have been associated with decreased cancer risk for breast, respiratory tract, and digestive tract cancers. In the digestive tract, reduced risk appears more likely in the upper tract.
Mechanisms under investigation include the role of secoiridoids such as oleuropein and decarboxylmethyl oleuropein, which may shift metabolic pathways toward better stress resistance. Higher phenolic content in extra virgin olive oil has been linked to a decreased ability of cancer cells to regenerate. Two phenols—tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol—may block matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MM-2), a step required for angiogenesis, limiting oxygen supply to tumours.
Investigating Polyphenols In Extra Virgin Olive Oil & Their Impact On Cancer
Dr Limor Goren and Dr David Foster explored the anti-cancer effects of oleocanthal, a phenolic compound in extra virgin olive oil that causes the peppery sensation at the back of the throat.
Their work showed oleocanthal can kill human cancer cells while sparing normal cells, likely by triggering lysosomal membrane permeabilisation, which releases digestive enzymes inside cancer cells and leads to cell death. Similar results were seen when using olive oil-enriched culture media. Oils with higher oleocanthal content were most effective in vitro; oils with average content reduced viability to a lesser extent; oils with no oleocanthal had no effect.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil And Breast Cancer
Dr Javier Menendez and colleagues at the Catalan Institute of Oncology investigated extra virgin olive oil on breast cancer cells. Using solid-phase extraction, they isolated polyphenols from commercially available oils and tested them on HER2-positive and HER2-negative cell lines.
They found that polyphenols from extra virgin olive oil reduced HER2 protein levels and increased tumour cell death in HER2-positive cells. Single compounds, including hydroxytyrosol and tyrosol, also produced strong tumouricidal effects and reduced HER2 activation. The authors concluded that polyphenols from extra virgin olive oil may provide a basis for new HER2-targeting agents.
Why Extra Virgin Olive Oil Deserves a Place in Your Healthy Diet
Including extra virgin olive oil like Morocco Gold in your daily meals is a simple way to support long-term health. From protecting your heart and lowering blood pressure to improving bone strength and reducing cancer risk, its unique polyphenols deliver wide-ranging benefits. As part of a Mediterranean diet and a balanced lifestyle, it remains one of the most effective and natural choices for protecting your wellbeing.