Why Can Extra Virgin Olive Oil Reduce Your Risk Of Stroke?
Updated 13th March 2023
SUMMARY:
CONTENTS:
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil Linked To Reduced Risk Of Stroke
- Stroke Prevention: Dietary Choices Matter
- Monounsaturated Fats
- What Is It in Extra Virgin Olive Oil That Reduces Our Risk Of Stroke?
- Health Benefits of Polyphenol Oleuropein
Extra Virgin Olive Oil Linked To Reduced Risk Of Stroke
Stroke Awareness Month takes place throughout May, with an aim to raise awareness of the causes and signs of Stroke and offer support to anyone affected by this all-too-common condition.
At Morocco Gold, we wanted to do our part to mark Stroke Awareness Month by sharing research linking adherence to a Mediterranean Diet with reduced risk of stroke.
A Mediterranean Diet is known for its emphasis on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, beans, nuts, and of course extra virgin olive oil.
According to advice from Stroke.org.uk, you can reduce your risk of stroke by getting a good variety of fruit, vegetables, starchy food and protein in your diet.
Included in their guidance on how to eat a healthier diet is the following:
“We all need small amounts of fat and sugar in our diets, but too much can lead to weight problems. Food that has been fried in butter, oil or ghee will contain high amounts of fat. Use vegetable, nut and olive-based oils instead.”
The British Journal Of Nutrition
According to The British Journal of Nutrition, consuming Extra Virgin Olive Oil – which can account for up to 20% of calories in Mediterranean diets – is linked to a significantly reduced risk of stroke.
Stroke Prevention: Dietary Choices Matter

Stroke prevention is a massive challenge on a global scale. Every year, more than 795,000 people in the United States have a stroke. But, there are some simple changes you can make to your diet that have the potential to make a significant difference. Eat This, Not That reports that turning to olive oil as a monounsaturated fat source may be a wise step in reducing stroke. One study – which looked at 841,000 people – showed that olive oil was the only source of monounsaturated fat associated with a reduced risk of stroke.
Monounsaturated Fats
If a pair of carbon atoms in the fatty acid chain is linked by a double bond instead of a single bond, the fatty acid is described as monounsaturated. Fats rich in monounsaturates tend to be liquid at room temperature. Olive Oil is one of the richest sources of monounsaturated fatty acids.
Monounsaturated fats—omega-6s in the case of olive oil—are important because they help boost heart health. This is important for helping prevent health issues such as cardiovascular disease or stroke.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil, like Morocco Gold, can reduce your risk of stroke by protecting against high blood pressure and cholesterol. Another study from the University of Bordeaux in France asked 7,625 people over the age of 65 how often they used olive oil in their cooking. After following up data from the participants medical records for the next five years, they discovered that stroke risk was 41% lower in those who regularly used olive oil compared to those who did not use it at all.
What Is It in Extra Virgin Olive Oil That Reduces Our Risk Of Stroke?

It is widely believed that the presence of polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil account for its ability to lower oxidized low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or ‘bad cholesterol’. It is high cholesterol levels which are a known risk factor for stroke.
Beneficial roles of natural plant polyphenols in the human body have been well known for millenia. Their sources are fresh fruits, vegetables and certain processed plant foods.
Polyphenols have been reported to reduce morbidity and slow down the progression of cardiovascular, neurodegenerative and cancer diseases.
Oleuropein, hydroxytyrosol, and their derivatives are polyphenolic compounds that are abundant in extra virgin olive oil. They are powerful antioxidants displaying anticancer, anti-angiogenic and anti-inflammatory properties.
Healthy blood pressure levels are an indicator of how clear the body’s arteries are. When blood pressure levels get out of balance, they can signal a potential heart attack or stroke. High bp levels are often caused by atherosclerosis, also called hardening of the arteries, which occurs when oxidized particles of LDL cholesterol stick to the walls of the arteries. Eventually these particles build up and form plaque, narrowing the blood vessels and putting a heavier workload on the heart as it pumps oxygenated blood to the entire body.
One of the specific compounds in extra virgin olive oil that directly combats this build-up is the polyphenol oleuropein. Oleuropein has been found by scientists to prevent the LDL cholesterol from oxidizing and sticking to the arterial walls.
Oleuropein
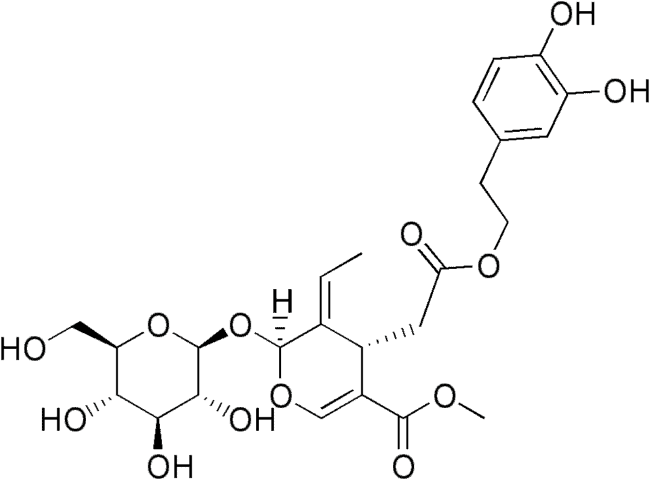
Oleuropein is a natural phenolic compound found in olive leaves and green olives, including the olive’s skin and flesh, from which olive oil is transferred. It causes the bitter taste in Extra Virgin olive oil.
Health Benefits of Polyphenol Oleuropein
Oleuropein health benefits include anti-oxidant and natural anti-inflammatory activity, low blood glucose values and free radicals removal. In addition, oleuropein has been linked to cardioprotective and neuroprotective activity.
Oleuropein belongs to a group of coumarin derivative called secoiridoids. It was found to be effective against various strains of bacteria, viruses, fungi and also moulds or even parasites. Oral treatment with oleuropein results in a decreased number of blood vessels proving strong anti-angiogenic properties. Phenolic compounds (oleuropein, protocatechuic acid) in extra virgin olive oil have also been shown to inhibit macrophage-mediated LDL oxidation. Leaf and olive fruit extracts containing oleuropein protect insulin-producing β-cell line (INS-1) against the deleterious effect of cytokines.






