Why Olive Oil Is So Important In The Mediterranean Diet
Updated August 12th 2021

We examine how the unsaturated fats vs saturated fat in extra virgin olive oil reduces the risk factors for ldl cholesterol (bad cholesterol) and heart disease when taken as part of a Mediterranean diet. Extra virgin olive oil like Morocco Gold is also high in oleic acid and polyphenols, the antioxidants that protect against damaging free radicals and provide a range of health benefits. So is olive oil good for you?
Including a high-quality olive oil is a vital part of healthy diet and there is ever mounting evidence to support this claim. In fact, whether consumed as part of The Mediterranean Diet or not, extra virgin olive oil is without question the healthiest of all fats available.
Olive Oil: The Best Fat For A Healthy Diet
Fats are made up of fatty acids and glycerol. A fatty acid consists of a chain of carbon atoms, where each carbon atom in the chain is attached to hydrogen atoms. The number of hydrogen atoms per carbon atom determines whether the fatty acid is saturated or unsaturated and therefore will contribute towards a healthy diet. Olive Oil is a source of monounsaturated fatty acids and is one of the healthiest components of The Mediterranean Diet.

How The Mediterranean Diet Can Reduce Weight Gain And Boost Health
Adding extra virgin olive oil to your healthy diet provides your body with important nutrients and all the healthy fats it needs. This reduces the cravings that lead to nutrient-empty foods like soft drinks, cookies and breads.
Extra virgin olive oil reduces the risk of acid reflex and prevents gastric juices from traveling back up from the stomach to the oesophagus. Olive oil inhibits gastric acid’s motility (the ability to move food through the digestive tract). Because of this, the stomach’s gastric content releases more gradually and slowly into the duodenum, making one feel fuller and benefiting from full nutrient absorption in the intestine. By emphasizing nutrient-rich extra virgin olive oil alongside vegetables and protein in your diet, you can avoid excess consumption of weight-inducing sugars and grains.
By feeding your body the healthy fats it needs and increasing your intake of olive oil, research shows you will feel fuller for a longer period of time and be less tempted to overeat, making extra virgin olive oil an important aid in weight loss and improved health for adults and children alike.
On the other hand, consumption of man-made trans fats found in hydrogenated and refined vegetable oils interferes with numerous biochemical processes in the body and can cause serious health problems and contribute to weight gain. Using extra virgin olive oil as part of a healthy diet can instead begin reversing the negative effects of trans fats.
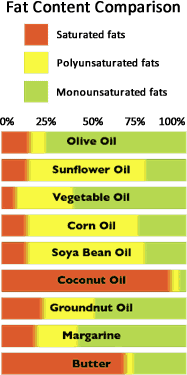
Where Olive Oil Sits In The ‘Fat League Table’.
1/ Saturated fats
If a fatty acid has all of the hydrogen atoms it can hold (2 per carbon atom in the chain) and all of the carbon atoms in the chain are linked by single bonds, it is described as saturated.
Saturated fats are usually solid or semi-solid at room temperature and are strongly associated with raised blood cholesterol which is why nutritionists recommend eating them as little as possible. Lard, butter, hard cheeses, whole milk, animal fats and palm and coconut oils – plus products containing them – all contain high levels of saturated fat that do not support a healthy diet.
2/ Monounsaturated Fats Support A Healthy Diet
If a pair of carbon atoms in the fatty acid chain is linked by a double bond instead of a single bond, the fatty acid is described as monounsaturated. Fats rich in monounsaturates tend to be liquid at room temperature. Olive oil is one of the richest sources of monounsaturated fatty acids and therefore supports a healthy diet.
Monounsaturated fats—omega-6s in the case of olive oil—are important because they help boost heart health. This is important for helping prevent health issues such as cardiovascular disease or stroke.
3/ Polyunsaturated fats
These contain more than one double bond and are liquid at room temperature. The main sources are vegetable oils, such as sunflower oil, corn oil and rapeseed, but not tropical oils such as coconut, palm and palm kernel oils.
4/ Trans fats
Trans fats are created when a hydrogenation process is applied to solidify oil for use in margarines or to improve a product’s shelf life. This processing causes trans fats to act like saturated fats.
The following illustrates the differing fat contents of a range of products.
What Is In 1 Tablespoon Of Extra Virgin Olive Oil?
One serving or 1 tablespoon of extra-virgin olive oil contains the following:
- 120 calories
- 10 grams of monounsaturated fat
- 2 grams of saturated fat
- 2 grams of polyunsaturated fat
- 1.9 milligrams of vitamin E (10 percent of Daily Value)
- 8.1 micrograms of vitamin K (10 percent of DV)
Not All Calories Are Created Equal
As part of maintaining a healthy diet many people want to know how many calories are in olive oil. Research has shown that not all calories are necessarily equal.
In a famous study at Middlesex Hospital in London in the 1950s, two British researchers, Professor Alan Kekwick and Dr. Gaston L.S. Pawan, tested a series of diets on overweight patients. The patients on a high-carbohydrate diet consistently gained or sustained weight, even when given limited calories. Conversely, subjects on a high-fat diet lost considerably more weight than any of the other diets, even when provided with excess calories.
A more recent study published in The Journal of the American Medical Association also challenges the notion that a “calorie is just a calorie.” Led by Cara Ebbeling, PhD, associate director and David Ludwig, MD, director of the New Balance Foundation Obesity Prevention Center at Boston Children’s Hospital, the purpose of the study was to learn what kind of diet helped people maintain their new weight after successfully losing weight. The results indicated that a low-fat diet predicts weight regain, while diets featuring a moderate to high percentage of calories from fat both increased subjects’ energy expenditure and reduced the surge in their blood sugar after eating, making these diets preferable to a low-fat diet for those trying to achieve lasting weight loss.
Is It Time To Increase Your Olive Oil Intake?
If you are convinced by the science (and let’s face it – it’s hard not to be!), you may be ready to boost your daily consumption of olive oil. So why not reach for the very best quality extra virgin olive oil around? Morocco Gold is a single source extra virgin olive oil of exceptional quality, extraordinary health benefits and a taste like none other.
