Another Of The Magic Ingredients Of Morocco Gold Extra Virgin Olive Oil that delivers incredible health benefits
Updated May 25th 2023

Summary:
- Polyphenols are micronutrients, packed with antioxidants, that are found in plants.
- The polyphenol oleocanthal, is only found in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) and is arguably the most important polyphenol that is naturally found in genuine extra virgin olive oil like Morocco Gold.
- Oleocanthal in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) has strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Its anti-inflammatory action on the body is very similar to ibuprofen.
- Oleocanthal in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) is believed to be responsible for the lower incident of chronic anti-inflammatory conditions in those who consume the Mediterranean diet.
- Studies have shown that oleocanthal specifically kills human cancer cells, but not normal, non-cancerous cells.
- It’s important to note that while oleocanthal in extra virgin olive oil contributes to the health benefits of extra virgin olive oil, it is just one of many beneficial compounds present. The combination of polyphenols, monounsaturated fats, and other bioactive components in extra virgin olive work synergistically to provide its overall health-promoting effects.
Contents:
- What Is Polyphenol Oleocanthal (p-HPEA-EDA)?
- Polyphenol Oleocanthal In Extra Virgin Olive Oil
- Studies On The Effect Of Polyphenol Oleocanthal In Extra Virgin Olive Oil On Cancer
- Anti-inflammatory Effects Of Oleocanthal In Extra Virgin Olive Oil
- Antioxidant Activity Of Oleocanthal In Extra Virgin Olive Oil
- Cardiovascular Health Benefits Of Oleocanthal In Extra Virgin Olive Oil
- Neuroprotective Effects Of Oleocanthal In Extra Virgin Olive Oil
- How Much Extra Virgin Olive Oil Should Be Taken?
What Is Polyphenol Oleocanthal (p-HPEA-EDA)? ?
Polyphenols are micronutrients, packed with antioxidants, that are found in plants. They can be found in antioxidant rich foods and there are more than 500 known polyphenols. The health benefits of these “lifespan essentials” protect your body, reduce your risk of chronic disease, and promote longevity.
Oleocanthal is a phenolic compound found in extra virgin olive oil, particularly in freshly pressed oil. It is responsible for the distinctive peppery and slightly bitter taste of high-quality olive oil. Like other polyphenols in olive oil, oleocanthal offers various health benefits.
p-HPEA-EDA, otherwise known as Oleocanthal, belongs to the Tyrosol family of polyphenols. It is the dialdehydic form of decarboxymethyl ligstroside aglycone. It is synonymous with p-HPEA-Elenolic acid Di-Aldehyde and Ligstroside-aglycone di-aldehyde. Its chemical formula is C17H20O5.
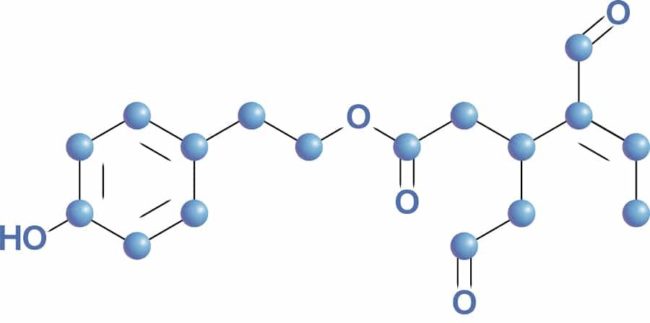
The Oleocanthal molecule is responsible for the peppery / stinging sensation at the back of your throat when you ingest certain extra virgin olive oils. In fact, this is how the molecule got its name, ’oleo’ means oil and ‘canth’ is Greek for stinging or prickly.
Polyphenol Oleocanthal In Extra Virgin Olive Oil
This polyphenol is only found in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO). It is a specific (and arguably the most important) polyphenol that is naturally found in truly extra virgin olive oil like Morocco Gold.
Oleocanthal was discovered in 1993 by Dr Gary Beauchamp when he was testing solutions of ibuprofen and found that it tasted similarly to freshly pressed extra virgin olive oil (EVOO). It turns out, the oleocanthal compound is highly similar to ibuprofen, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, and has similar effects.
Oleocanthal is not present in the olive fruit itself but is only created when the olives are cold-pressed. This medicinal type of extra virgin olive oil is what attributes to low rates of both cancer and cognitive diseases in Mediterranean populations. The importance and uniqueness of Oleocanthal in extra virgin olive oil is that it has strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Its anti-inflammatory action on the body is very similar to ibuprofen, one of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs most widely consumed.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) such as aspirin, paracetamol and ibuprofen, can be differentiated from steroids because they have far fewer secondary effects. NSAIDS have proven to have very beneficial effects in diseases that involve chronic inflammation processes, such as degenerative and neurodegenerative illnesses (Alzheimer).
Oleocanthal is being used medicinally in Europe for its pharmacological qualities. The risk of chronic inflammatory disease in Mediterranean populations are the lowest in the world and life expectancy amount the highest. (WHO World Health Statistics of 2010). This type of polyphenol in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) is believed to be responsible for the lower incident of chronic anti-inflammatory conditions in those who consume the Mediterranean diet.
Studies On The Effect Of Polyphenol Oleocanthal In Extra Virgin Olive Oil On Cancer
Many studies have identified the components of extra virgin olive oil which confer health benefits, but few have tested the effect of high phenolic extra virgin olive oil on cancer. This is a gap which the research of Dr Limor Goren who recently completed her PhD, and her colleagues at City University of New York set out to explore.
The study explored the effects of oils containing varying levels of oleocanthal on anti-cancer effects. Dr Goren’s study showed that extra virgin olive oil rich in oleocanthal are powerful enough have an effect on cancer cells, while oleocanthal-poor olive oils do not.
The study has shown that oleocanthal specifically kills human cancer cells, but not normal, non-cancerous cells. The authors suggest that this is due to the ability of oleocanthal to induce the death of cancer cells through lysosomal membrane permeabilisation (LMP). (A lysosome is a membrane-bound cell organelle that contains digestive enzymes. Lysosomes are involved with various cell processes. They break down excess or worn-out cell parts. They may be used to destroy invading viruses and bacteria). Permeabilising the lysosomal membrane allows digestive enzymes stored inside this organelle to be released, which preferentially causes cell death in cancer cells.
Furthermore, recognising that different olive oils have different concentrations due to their origin, harvest time, and processing methods, the researchers tested a variety of extra virgin olive oils to determine their respective concentrations of oleocanthal, which ranged from very low to very high.
The olive oils that had high oleocanthal content completely killed cancer cells in vitro (in a petri dish), in a manner similar to purified oleocanthal. The olive oils with average oleocanthal content reduced viability, but to a lesser extent. Those with no oleocanthal had no effect on cell viability.
In addition, Dr Goren and colleagues also found that injection of oleocanthal into mice engineered to develop pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours, reduced their tumour burden and extended the lifespan of the mice. More specifically, the injections extended the lives of the mice by an average of four weeks. Based on lifespan conversion, if oleocanthal has the same effect in humans, it might extend human life by more than 10 years.
A 2015 study by Dr. Paul Breslin shows how oleocanthal can kill cancer cells in as little as 30 minutes. Although it was always believed that extra virgin olive oil had combat cancer, it was also one of the first studies that showed how this happens. This study was published by the scientific journal, Molecular and Cellular Oncology, showing that oleocanthal creates cell rupture of cancer cells without hurting healthy cells.
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/23723556.2015.1006077
A similar study published by ACS Chemical Neuroscience showed oleocanthal presence combats Alzheimer’s disease https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/cn400024q
Striking results were seen according to the World Olive Center for Health website (https://worldolivecenter.com/great-announcements-on-the-beneficial-properties-of-olive-oil-at-the-olympia-health-and-nutrition-international-awards-ceremony-in-the-old-parliament-in-athens/) which showed “decrease or stabilization of white blood cells, a specific death of cancer cells, and a fall in cancer markers in a significant number of patients.
This is the first time the world has seen such strong indications about the health properties of oleocanthal olive oil in oncology patients”
Anti-inflammatory Effects Of Oleocanthal In Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Oleocanthal in extra virgin olive oil has been shown to possess powerful anti-inflammatory properties. It works by inhibiting enzymes called cyclooxygenases (COX), similar to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen. By reducing inflammation in the body, oleocanthal may help alleviate symptoms associated with chronic inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Antioxidant Activity Of Oleocanthal In Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Oleocanthal in extra virgin olive oil acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. By neutralizing these harmful compounds, it helps prevent oxidative stress and cellular damage, which can contribute to chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and aging-related conditions.
Cardiovascular Health Benefits Of Oleocanthal In Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Similar to oleuropein, oleocanthal in extra virgin olive oil has been linked to cardiovascular benefits. It promotes vasodilation, helping to relax blood vessels and improve blood flow, which can reduce blood pressure and enhance cardiovascular health. It also exhibits antiplatelet activity, preventing excessive blood clotting that can lead to heart attacks or strokes.
Neuroprotective Effects Of Oleocanthal In Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Oleocanthal in extra virgin olive oil has shown potential neuroprotective effects, particularly in the context of age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases. It has been found to help clear the accumulation of abnormal proteins, such as beta-amyloid plaques, which are associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties may contribute to brain health and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative conditions.
How Much Extra Virgin Olive Oil Should Be Taken?
In order that oleocanthal may have protective effects on our health, like the rest of extra virgin olive oil polyphenols, a daily and a regular consumption is recommended. Four daily tablespoons of an extra virgin olive oil rich in Oleocanthal is equivalent to a consumption of 125 mg of ibuprofen, which would be, according to the researchers of the Andalusian society of Oleocanthal, a good basis to prevent or relieve chronic inflammatory processes and reduce the risks of cancer.
This continues our series of articles about the polyphenol content of our new harvest extra virgin olive oil and what they can do to improve our health. As we have reported, this year’s harvest has produced a low acidity level of 0.2% together with the highest level of polyphenols yet seen in our extra virgin olive oil of 644 mg/kg
