Explores the evidence-based health benefits of the polyphenols found in Morocco Gold extra virgin olive oil
Updated January 26th 2023

Summary:
- What are Phenols? Phenols are broadly a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. When a phenolic compound forms a larger, repetitive chain it then becomes a polyphenol. Polyphenols present powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that make them natural and efficient anticancer agents to be found in a well-balanced diet like the Mediterranean diet.
- The polyphenols in Morocco Gold extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) and their associated health benefits include:
- Oleocanthal in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) which is a natural phenolic compound found only in olive oil, hence the prefix “oleo”. It is believed to cause the pungent sensation in olive oil’s flavour. Oleocanthal has been shown to act as an anti-inflammatory agent and also has anti-oxidant properties.
- Oleacein in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) has been linked to antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative and antimicrobial activity. Additionally, it has been found to decrease the progression of atherosclerosis
- Tyrosol, which is mostly found in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) protects against free radical cells as well as activating antioxidant systems in the body.
- Hydroxytyrosol in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) has been shown to inhibit human colon adenocarcinoma cells as well as breast cancer cells.
- Oleuropein in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) health benefits include anti-oxidant and natural anti-inflammatory activity, low blood glucose values and free radicals removal. In addition, oleuropein has been linked to cardioprotective and neuroprotective activity.
- Ligstroside Aglycone (LA) in extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects in osteoarthritis and the perpetuation of chronic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis.
What are Phenols?
The olive fruit, just like numerous other fruit, vegetables, grains, legumes and seaweeds, contains a specific type of chemical compounds called phenols or phenolic compounds.
Phenols are broadly a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group, for example Oleocanthal. When a phenolic compound forms a larger, repetitive chain it then becomes a polyphenol.
There is enormous variation among phenolic compounds that can be found in a wide range of foods. However, different types of polyphenols have different impact on human health. In olive oil with high phenolic content we can find specific polyphenols that have been shown to have many health benefits.
There is a growing body of evidence for beneficial roles of natural plant polyphenols in the human body. Natural bioactive polyphenols are compounds of varied chemical structures. Polyphenols are arguably the largest group of chemical substances in the plant kingdom.
There are more than 8000 different polyphenolic structures known, including several hundred isolated from edible plants. Their sources are, among others, fruits, vegetables, nuts and seeds, roots, bark, leaves of different plants, herbs, whole grain products, as well as tea, coffee, and red wine.
These compounds are characterized by a broad spectrum of biological activities. The beneficial impact of vegetables, fruits, and herbs on human health has been well known for centuries. Today, we understand the reasons for that as many plant-derived products are rich in nutrients, vitamins, minerals, and very importantly, bioactive polyphenols.
Polyphenols present powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that make them natural and efficient anticancer agents to be found in a well-balanced diet. Unlike vitamins and minerals, polyphenols are not the essential elements of the primary plant metabolism. Natural polyphenolic compounds are rather products of the secondary plant metabolism. Anyhow, they do play critical metabolic roles in the human organism.
Polyphenols have been shown to reduce morbidity and/or slow down the progression of cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and cancer diseases. The mechanism of action of polyphenols strongly relates to their antioxidant activity. Polyphenols are known to decrease the level of reactive oxygen species in the human body. In addition, health-promoting properties of plant polyphenols comprise anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, anti-atherogenic, anti-thrombotic, and anti-mutagenic effects. There is a body of research demonstrating their ability to modulate the human immune system by affecting the proliferation and activity of white blood cells, as well as the production of cytokines or other factors that participate in immunological defence.
The polyphenols in olive oil are especially interesting with respect to their well-established beneficial effects on human health and metabolism, as well as the popularity of olive oil in many different diets, and specifically the Mediterranean diet.
The Chemical Composition Of Olive Oil
The chemical composition of olive oil varies depending on the extraction technology that is applied in order to obtain the oil form the fruits. The process of extraction of olive oil depends on crushing olives and then separating the oil from the fruit pulp under pressure.
Morocco Gold EVOO is produced by only by mechanical means at a temperature below 28 degrees C. It is not further processed in any other way. Extra virgin olive oil by its low yield is typically more expensive than other types of olive oil, but it contains the highest level of polyphenols.
It is also unfiltered. Unfiltered extra virgin olive oil preserves additional polyphenols of higher polarity that are typically lost with small amounts of water that are removed when filtered.
The quantity and quality of polyphenols in olive oil is closely related to the process of olive milling and further processing. Therefore, virgin olive oils have substantially higher amounts of polyphenols than refined olive oils. Phenolic compounds are mainly responsible for the characteristic peppery, slightly bitter taste associated with high quality extra virgin olive oils.
What Kind of Polyphenols Does Olive Oil Contain?
Various high phenol foods contain a wide range of phenolic compounds in various concentrations. Naturally, olive oil with high phenolic content has been thoroughly researched to see the health benefits of polyphenols. As a result, the most abundant of polyphenols, unique to olive oil, have been identified, and include:
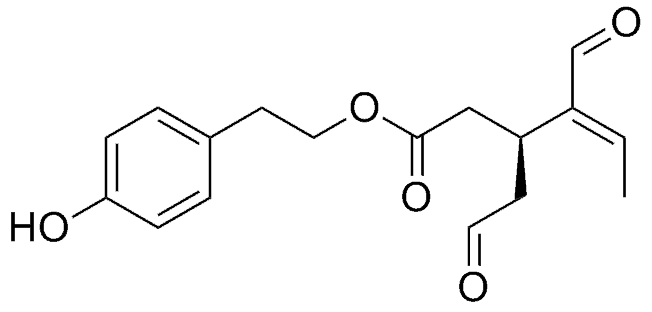
Oleocanthal is a natural phenolic compound found only in olive oil, hence the prefix “oleo”. It is believed to cause the pungent sensation in olive oil’s flavour. Oleocanthal is a tyrosol ester.
Health Benefits of Oleocanthal
According to studies, oleocanthal has been observed to act as an anti-inflammatory agent and also has anti-oxidant properties. Furthermore, oleocanthal-rich olive oil has been observed to cause a rupture of cancerous cells, releasing enzymes and causing cell death, without harming healthy cells. Oleocanthal has been found to enhance a potential neuroprotective mechanism against Alzheimer’s Disease.
2/ Oleacein
This natural phenolic compound has been found both in olive oil and in jasmine. It is among the most abundant phenolic compounds in Extra Virgin olive oil.
Health Benefits of Oleacein
Oleacein has been linked to antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative and antimicrobial activity. Additionally, it has been found to decrease the progression of atherosclerosis
3/ Tyrosol
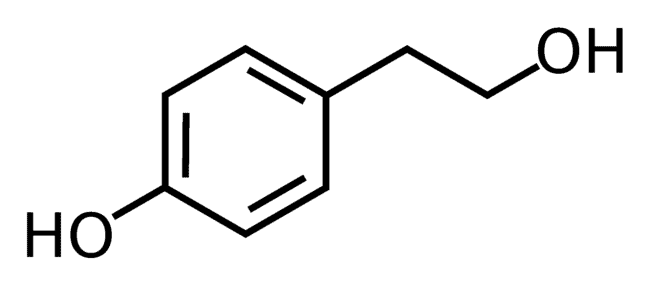
Tyrosol is a natural antioxidant that can be found in numerous sources, although it is mainly found in Extra Virgin olive oil.
Health Benefits Of Tyrosol
Its beneficial properties for human health are strongly related to the ability of the molecule to scavenge free radicals and reactive oxygen/nitrogen species as well as to activate endogenous antioxidant systems in the body. Free radical scavenging properties have been convincingly confirmed in studies on rats with alloxan-induced diabetes mellitus.
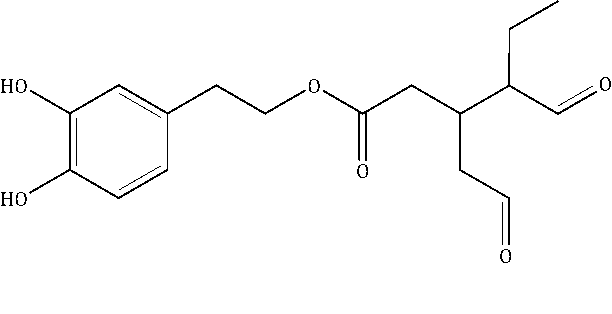
4/ Hydroxytyrosol
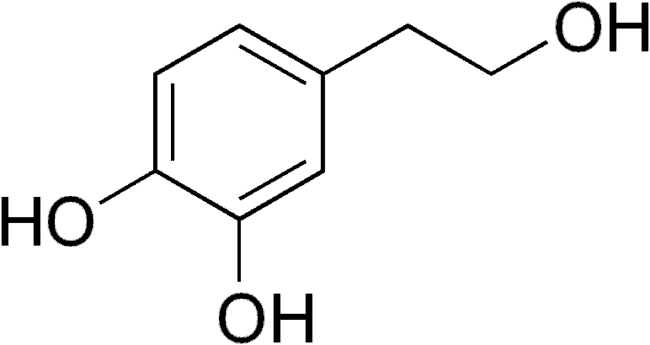
Hydroxytyrosol is a phenylethanoid, a type of phenolic phytochemical believed to be one of the most powerful natural antioxidants. Having three hydroxyl groups it is often referred to as a polyphenol, although it is quite a small molecule in comparison to many other natural polyphenols. Pure hydroxytyrosol is clear, colorless, and liquid and mixes with either aqueous or fatty matrices.
Hydroxytyrosol (CAS number: 10597-60-1; IUPAC name: 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1,2-benzenediol; other names include: 3-hydroxytyrosol 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethanol (DOPET), 4-hydroxytyrosol, as well as the abbreviation ’HT’) is the major phenolic component of olives, which originates from the hydrolysis of another olive component, oleuropein, during the maturation of olives, during the storage of olive oils, and also during the preparation of olives for consumption. The oleuropein component loses glucose to form aglycone, which then converts to hydroxytyrosol and elenolic acid.
Health Benefits of Hydroxytyrosol
Treatment of human colon adenocarcinoma cells with olive oil polyphenols significantly inhibits cell proliferation. In spite of the relatively low concentrations of hydroxytyrosol in olive oil, polyphenols are in high micromolar concentration range in the colon after gastric hydrolysis and colonic fermentation of secoiridoids that are naturally present in olive oil.
In colon cancer cells HT reduces epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) level by promoting its degradation. EGRF is one of the key receptors triggering colon carcinogenesis as it regulates the proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and invasion of cancer cells. Moreover, HT was found to be an effective cytotoxic agent in breast cancer cell models.
5/ Oleuropein
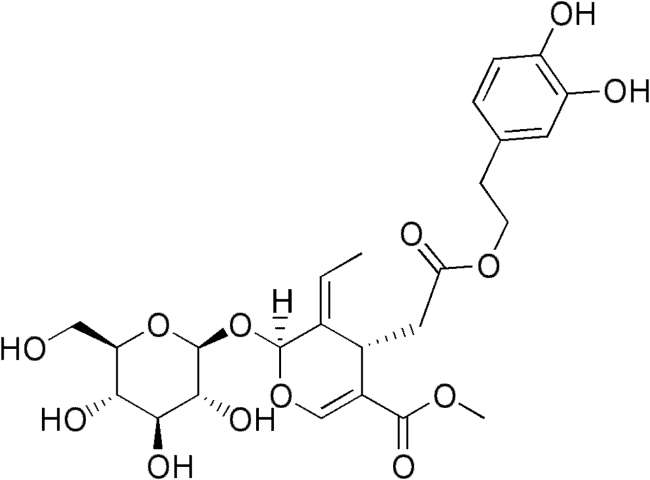
Oleuropein is a natural phenolic compound found in olive leaves and green olives, including the olive’s skin and flesh, from which olive oil is transferred. It causes the bitter taste in Extra Virgin olive oil.
Health Benefits of Oleuropein
Oleuropein health benefits include anti-oxidant and natural anti-inflammatory activity, low blood glucose values and free radicals removal. In addition, oleuropein has been linked to cardioprotective and neuroprotective activity.
Oleuropein belongs to a group of coumarin derivative, secoiridoids. It was found to be effective against various strains of bacteria, viruses, fungi and also molds or even parasites. Oral treatment with oleuropein results in a decreased number of blood vessels proving strong anti-angiogenic properties. Phenolic compounds (oleuropein, protocatechuic acid) of virgin olive oil have also been shown to inhibit macrophage-mediated LDL oxidation. Leaf and olive fruit extracts containing oleuropein protect insulin-producing β-cell line (INS-1) against the deleterious effect of cytokines.
Oleuropein as Anticancer Agent
There are numerous studies confirming the anticancer activity of oleuropein, as observed in human cancer cell lines, such as: breast adenocarcinoma, melanoma, urinary bladder carcinoma, colorectal adenocarcinoma, prostate cancer, lung carcinoma, glioblastoma, renal cell adenocarcinoma and glioma.
Oleuropein was found to display antiproliferative, proapoptotic effects, overall anticancer activity, and specifically an ability to decrease cancer cell viability, as well as induction of cancer cell apoptosis. Oleuropein induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells via the p53-dependent pathway and through the regulation of Bax and Bcl2 genes. Therefore, oleuropein may have a great therapeutic potential for breast cancer treatment.
6/ Ligstroside Aglycone
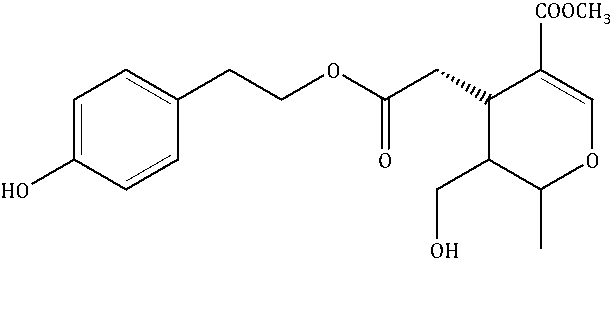
It belongs to the class of organic compounds known as phenolic glycosides. The phenolic structure is attached to a glycosyl moiety. Ligstroside can be found in olives and in smaller amounts in other fruit.
This polyphenol is synonymous with p-HPEA-Elenolic acid. It is a member of the Tyrosol family of polyphenols and has the chemical formula : C19H22O7
While information on LA bioactivity is limited, a few years ago, LA was demonstrated to behave as an antioxidant. Furthermore, LA has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects by controlling and downregulating NF-κB (NF-kB is a type of DNA that is thought to play a pivotal role in the initiation of osteoarthritis and the perpetuation of chronic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis) as well as the potential to induce a caloric restriction-like state that affects the muscle, brain, fat tissue and kidney, particularly through activation and increased levels of sirtuins. (Sirtuins are a family of proteins that regulate cellular health. They play a key role in regulating cellular homeostasis, keeping cells in balance).
Polyphenols And The Mediterranean Diet
Epidemiological studies show that people of the Mediterranean region have a lower incidence of several cancers when compared to other populations. The consumption of olive oil is an important factor in the Mediterranean diet and is generally believed to be beneficial for health.
Olive oil consumption was proven to prevent from colorectal cancer, breast cancer and skin cancer. Several mechanisms of antitumor activity of extra virgin olive oil have been determined. Interestingly, olive oil polyphenols were proven to protect biological membranes against oxidative modification and losing structural integrity. Similarly, polyphenolic compounds decreased oxidative damage to cellular DNA effectively decreasing promotion of colon cancer.
In Summary
Beneficial roles of natural plant polyphenols in the human body have been well known for millenia. Their sources are fresh fruits, vegetables and certain processed plant foods.
Polyphenols have been reported to reduce morbidity and slow down the progression of cardiovascular, neurodegenerative and cancer diseases.
Oleuropein, hydroxytyrosol, and their derivatives are polyphenolic compounds that are abundant in olive oil. They are powerful antioxidants displaying anticancer, anti-angiogenic and anti-inflammatory properties.
An increase in consumption of virgin olive oil and other plant products rich in polyphenolic compounds, specifically in populations with low olive oil intake, will undoubtedly provide much needed and diverse health benefits.
