Shows how including extra virgin olive oil rich in polyphenols provides health benefits for the cardiovascular system
Updated May 13th 2024
Summary
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil Can Help Prevent Cardiovascular Diseases
- Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number 1 cause of death globally: more people die annually from CVDs than from any other cause
- Chronic inflammation is a risk factor for many types of cardiovascular disease, and Extra Virgin Olive Oil has well-documented anti-inflammatory properties
- Extra virgin olive oil has been listed as one of seven diet tips to help prevent deep vein thrombosis
- Studies have shown that those who consume a diet rich in polyphenols such as those found in extra virgin olive oil are at a lower risk for developing deep vein thrombosis.
Contents
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil And Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil And Cardiovascular Diseases?
- What Are Cardiovascular Diseases?
- How Extra Virgin Olive Oil Helps To Protect Against CVD
- Polyphenols – Extra Virgin Olive Oils Powerful Antioxidant
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil And The Cardiovascular System
Extra Virgin Olive Oil And Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis is a condition characterized by the formation of blood clots in the deep veins of the body, typically the legs. These clots can cause pain, swelling, and, if dislodged, can travel to the lungs, creating a potentially life-threatening situation known as a pulmonary embolism. Given the severity of DVT, finding effective prevention strategies is paramount.
Extra virgin olive oil stands out in the culinary world for its rich flavour and health benefits. It’s the highest quality olive oil, obtained through cold pressing without the use of chemicals or excessive heat, ensuring it retains its beneficial antioxidants and monounsaturated fats. Among these are oleic acid and phenolic compounds, which have been identified as powerful agents in promoting cardiovascular health.
Extra virgin olive oil has been listed as one of seven diet tips to help prevent deep vein thrombosis. According to a new report in Everydayhealth.com, could reduce the risk of blood clots forming inside the body. Citing a study from the National Institutes of Health–funded study presented March 7, 2019, at the American Heart Association’s Epidemiology and Prevention Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health Scientific Sessions, it says:
Consuming olive oil at least once a week reduced platelet activity in nonsmoking obese adults (those with a body mass index, or BMI over 30), a sign that this oil may lower the risk of a blood clot.
Similarly, an earlier study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that antioxidants called polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil helped prevent blood clots. In the study, people who consumed virgin olive oil with a high phenol content had lower levels of a substance that promotes blood clots. And the good news is that Morocco Gold extra virgin olive oil has some of the highest levels of polyphenols around.
Extra virgin olive oil is a natural product made from the olives that grow on olive trees. The oil is extracted from the olives using a process that does not involve any chemicals or artificial additives. extra virgin olive oil is considered to be the highest quality olive oil available and is rich in nutrients, including polyphenols.
Deep vein thrombosis is a serious condition that can occur when blood clots form in the veins, usually in the legs. If these clots break loose and travel to the lungs, they can cause a pulmonary embolism, which can be fatal. While there are many factors that can contribute to the development of deep vein thrombosis, studies have shown that those who consume a diet rich in polyphenols are at a lower risk for developing this condition.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil And Cardiovascular Diseases?
What are cardiovascular diseases?
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number 1 cause of death globally: more people die annually from CVDs than from any other cause.
An estimated 17.9 million people died from CVDs in 2016, representing 31% of all global deaths. Of these deaths, 85% are due to heart attack and stroke.
Most cardiovascular diseases can be prevented by addressing behavioural risk factors such as tobacco use, unhealthy diet and obesity, physical inactivity and harmful use of alcohol using population-wide strategies.
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) – World Health Organization
CVDs are a group of disorders of the heart and blood vessels. They include:
- Coronary heart disease – disease of the blood vessels supplying the heart muscle;
- Cerebrovascular disease – disease of the blood vessels supplying the brain;
- Peripheral arterial disease – disease of blood vessels supplying the arms and legs;
- Rheumatic heart disease – damage to the heart muscle and heart valves from rheumatic fever, caused by streptococcal bacteria;
- Congenital heart disease – malformations of heart structure existing at birth;
- Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism – blood clots in the leg veins, which can dislodge and move to the heart and lungs.
At the age of 24, your risk for CVD is just 20%. By age 45, your chances more than double to 50%. Over the age of 80, 90% of individuals have some form of CVD.
In 2016, the cost of CVD in the USA alone was around $555Bn. This is expected to rise to $1.1Tr by 2035.
How Extra Virgin Olive Oil Helps To Protect Against CVD
The increased focus on healthy food and healthy diet has seen more food lovers turn towards diets like the Mediterranean diet and the Keto diet. Whether this is for specific health reasons, a diet to lower cholesterol, a diet for high blood pressure, a diet for weight loss or for overall wellness one of the key constituents that remains a constant is extra virgin olive oil, the original superfood.
What makes extra virgin olive oil so special is that it has stood the test of time as a superfood from the time of the ancients. Olive oil has long been considered sacred. The olive branch was often a symbol of abundance, glory, and peace. Over the years, the olive has also been used to symbolize wisdom, fertility, power, and purity.
In ancient Rome, olive oil was used for nearly everything in relation to their health. Roman medicine takes heavily from Greek doctors, who influenced European medicine for centuries, and Hippocrates, the father of modern medicine writes about over 60 different conditions or ailments that can be treated with olive oil.
Olive oil is now probably the most widely researched superfood on the planet and its many health benefits are evidence based and well understood. Thanks to the recent spotlight on the Mediterranean Diet, extensive research has been done on the phytonutrient composition of olive oil. What has been discovered is an extensive list of phytonutrients; one of the most praised is its polyphenols. The amount of polyphenols found in Extra Virgin Olive Oil is truly amazing!
Anti-inflammatory Properties
Chronic inflammation is a known precursor to various cardiovascular diseases, including the formation of blood clots. EVOO’s rich content of antioxidants, such as oleocanthal, has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties similar to ibuprofen. Regular consumption of EVOO can help reduce inflammation in the body, potentially lowering the risk of blood clot formation.
Improved Vascular Health
EVOO contributes to better vascular health by improving the lining of the blood vessels, thereby enhancing blood flow and reducing the chances of clot formation. The monounsaturated fats found in EVOO can help decrease LDL (bad) cholesterol levels while raising HDL (good) cholesterol, further protecting against the buildup of plaque and blood clots in the arteries.
Anticoagulant Effects
Recent studies suggest that the phenolic compounds in EVOO may have anticoagulant properties, which help prevent the blood from clotting too easily. This effect can be particularly beneficial for those at risk of DVT, offering a natural means of keeping the blood flowing smoothly and reducing the likelihood of clot formation.
Polyphenols – Extra Virgin Olive Oils Powerful Antioxidant
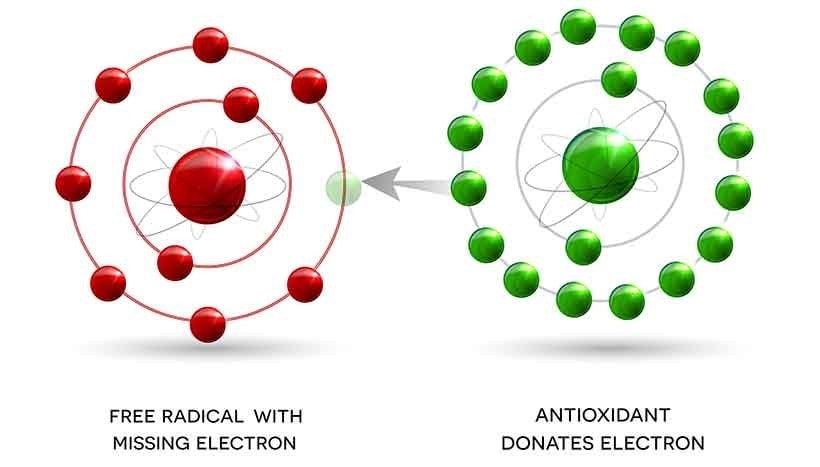
Polyphenols are a potent antioxidant – one that can decommission a nasty molecule in your body called free radicals. Free radicals can ricochet around inside your body and harm good cells. Antioxidants, such as the polyphenols found in Extra Virgin Olive Oil, work to neutralize free radicals; protecting the body from their harmful antics. These antioxidants circulate in the body, hooking up with free radicals, unstable compounds thought to play a role in more than 60 different health conditions including cancer and atherosclerosis, as well as aging.”
Most informed websites will point to the health benefits of regularly taking premium quality Extra Virgin Olive Oil like Morocco Gold. We have often discussed these health benefits with our customers at our tasting events. Many of the people we have met wish to know more, so here we are going to provide a series of articles that will provide the science behind what Extra Virgin Olive Oil actually does and why it is good for you. This first article will look at the cardiovascular system.
Structures of the Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system is responsible for transporting nutrients and removing gaseous waste from the body. This system is comprised of the heart and the circulatory system. Structures of the cardiovascular system include the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The lymphatic system is also closely associated with the cardiovascular system.
Heart
The heart is the organ that supplies blood and oxygen to all parts of the body. This amazing muscle produces electrical impulses through a process called cardiac conduction. These impulses cause the heart to contract and then relax, producing what is known as a heartbeat. The beating of the heart drives the cardiac cycle which pumps blood to cells and tissues of the body.
Blood Vessels
Blood vessels are intricate networks of hollow tubes that transport blood throughout the entire body. Blood travels from the heart via arteries to smaller arterioles, then to capillaries or sinusoids, to venules, to veins and back to the heart. Through the process of microcirculation, substances such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and wastes are exchanged between the blood and the fluid that surrounds cells.
Blood
Blood delivers nutrients to cells and removes wastes that are produced during cellular processes, such as cellular respiration. Blood is composed of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. Red blood cells contain enormous amounts of a protein called haemoglobin. This iron containing molecule binds oxygen as oxygen molecules enter blood vessels in the lungs and transport them to various parts of the body.
After depositing oxygen to tissue and cells, red blood cells pick up carbon dioxide (CO2) for transportation to the lungs where CO2 is expelled from the body.
Circulatory System
The circulatory system supplies the body’s tissues with oxygen rich blood and important nutrients. In addition to removing gaseous waste (like CO2), the circulatory system also transports blood to organs (such as the liver and kidneys) to remove harmful substances. This system aids in cell to cell communication and homeostasis by transporting hormones and signal messages between the different cells and organ systems of the body. The circulatory system transports blood along pulmonary and systemic circuits. The pulmonary circuit involves the path of circulation between the heart and the lungs. The systemic circuit involves the path of circulation between the heart and the rest of the body. The aorta distributes oxygen rich blood to the various regions of the body.
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is a component of the immune system and works closely with the cardiovascular system. The lymphatic system is a vascular network of tubules and ducts that collect, filter, and return lymph to blood circulation. Lymph is a clear fluid that comes from blood plasma, which exits blood vessels at capillary beds. This fluid becomes the interstitial fluid that bathes tissues and helps to deliver nutrients and oxygen to cells. In addition to returning lymph to circulation, lymphatic structures also filter blood of microorganisms, such as bacteria and viruses. Lymphatic structures also remove cellular debris, cancerous cells, and waste from the blood. Once filtered, the blood is returned to the circulatory system.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil And The Cardiovascular System
Lowering your risk of cardiovascular problems is an area upon which several recent studies on Extra Virgin Olive Oil have focused. Chronic inflammation is a risk factor for many types of cardiovascular disease, and Extra Virgin Olive Oil has well-documented anti-inflammatory properties.
One place we don’t want excessive ongoing inflammation is within our blood vessels. Our blood supply is just too important for maintaining the health of all our body systems, and it cannot effective support our body systems when compromised with ongoing inflammation. Given this relationship, it’s not surprising to see cardiovascular benefits of Extra Virgin Olive Oil rising to the top of the health benefits provided by this remarkable oil.
From a variety of different research perspectives we know that daily intake of Extra Virgin Olive Oil in amounts as low as one tablespoon per day reduces inflammatory processes within our blood vessels. By reducing these processes, Extra Virgin Olive Oil also reduces our risk of inflammation-related cardiovascular diseases like atherosclerosis.
Yet anti-inflammatory benefits are not the only cardiovascular benefits provided by Extra Virgin Olive Oil. Two other broad types of heart-related benefits are well documented for this oil. The first type is lessened risk of forming unwanted blood clots. While blood clotting is a natural and healthy process required for the healing of wounds and prevention of excessive bleeding, clotting in the arteries can ultimately result in a heart attack or stroke.
One risk factor for unwanted clotting in our arteries is excessive clumping together of our platelet blood cells. This clumping process is also called “aggregation.” Regular incorporation of Extra Virgin Olive Oil into a meal plan has been shown to lessen the risk of this excessive aggregation, and the reason that researchers refer to Extra Virgin Olive Oil as an “anti-aggregatory” oil.
The other broad area of cardiovascular benefits involves improved levels of circulating fats in our bloodstream, as well as protection of those fats from oxygen-related damage. Decreased levels of total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol following consumption of Extra Virgin Olive Oil are findings are the vast majority of studies that have analysed this relationship.
Yet equally important, the cholesterol molecules that remain in our blood also appear to be better protected from oxygen-related damage (oxidation). Since fats and cholesterol belong to a broader technical category called “lipids,” damage to the fats and cholesterol in our blood stream is typically referred to as “lipid peroxidation.” And it is precisely this lipid peroxidation process that gets reduced through incorporation of Extra Virgin Olive Oil into a meal plan.
Cardiovascular Disease
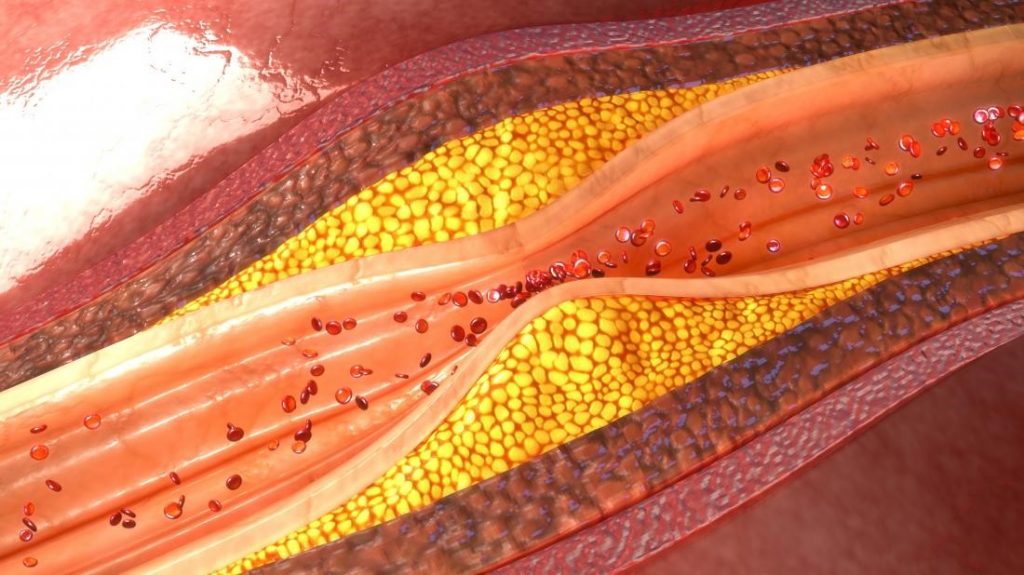
Atherosclerosis is the build-up of fatty plaques on the walls of arteries. Fatty plaque known as atheroma (yellow) has built-up on the inner wall and is blocking about 60% of the artery width. Atherosclerosis leads to irregular blood flow and clot formation, which can block the coronary artery resulting in heart attack.
According to the World Health Organization, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death for people world-wide. Cardiovascular disease involves disorders of the heart and blood vessels, such as coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease (stroke), elevated blood pressure (hypertension), and heart failure.
- Hypertension – persistently elevated blood pressure (high blood pressure) in the arteries. It is associated with the development of disorders such as atherosclerosis, heart attack, stroke, and can cause kidney damage.
- Atherosclerosis – artery walls become hardened due to build-up of plaque (fatty deposits). It causes decreased blood supply to tissues and may lead to blood clots, stroke, aneurysm, or heart disease.
- Aneurysm – a bulging in a weakened area of an artery that could rupture and cause internal bleeding.
- Coronary artery disease (heart disease) – narrowing or blockage in the coronary arteries, which supply blood directly to the heart muscle. Complete blockage of blood flow will cause a heart attack.
- Stroke – death of brain cells (neurons) due to lack of blood supply.
- Heart failure – the heart is not able to supply enough blood to body tissues. It is caused by conditions such as hypertension, heart disease, and cardiomyopathy (chronic disease of the heart muscle).
It is crucial that the organs and tissues of the body receive proper blood supply. Lack of oxygen means death, therefore having a healthy cardiovascular system is vital for life. In most cases, cardiovascular disease can be prevented or greatly diminished through behavioural modifications. Individuals wishing to improve cardiovascular health should consume a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and abstain from smoking.
Imagine your body as a highly complex, high-performance engine. High quality extra virgin olive oil like Morocco Gold is natures highest performance engine oil, to keep your body well- tuned and running smoothly over a lifetime.
The health benefits of extra virgin olive oil have been known for centuries. As discussed, studies have shown that the cardiovasular system also benefits from regular consumption of EVOO. In addition to reducing the risk of heart disease, consuming EVOO may also protect against other chronic diseases such as cancer. If you are looking for a healthy cooking oil that has multiple health benefits, extra virgin olive oil is a good choice.