Showing how the polyphenols in best olive oil – extra virgin olive oil delivers further health benefits
Updated December 13th 2023
Summary
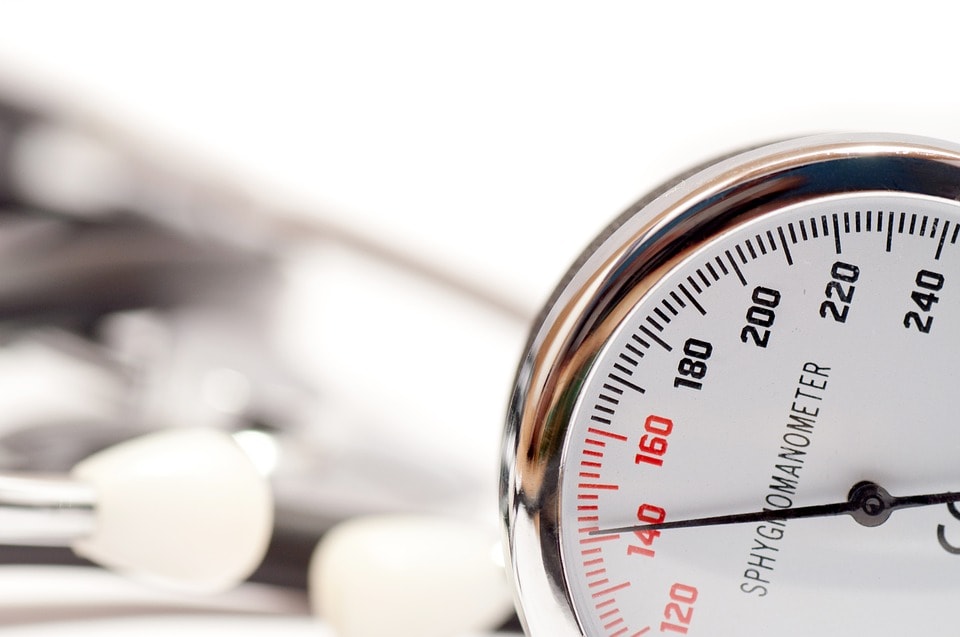
- Extra virgin olive oil listed as a top food to maintain healthy blood pressure, says new report.
- The best olive oil takes its place in Today.com list alongside 16 other foods in management of hypertension.
- Extra virgin olive oil provide blood-pressure lowering effects due to polyphenols and oleic acid, which may help reduce overall risk factors, like blood pressure, for heart disease.
- Morocco Gold’s latest harvest has produced a low acidity level of 0.2% together with an exceptionally high level of polyphenols.
Contents
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil Makes New List of Top Foods For Blood Pressure
- Why Diet Can Be As Crucial As Medication For Healthy Blood Pressure
- Why Extra Virgin Olive Oil Is One of Top Foods For Blood Pressure Control
- Morocco Gold Extra Virgin Olive Oil And Blood Pressure Control
- What Other Foods Can Lower Blood Pressure?
Extra Virgin Olive Oil Makes New List of Top Foods For Blood Pressure
Extra virgin olive oil has made the list of top foods to maintain healthy blood pressure, according to a new report on Today.com
The list, which includes 16 other essential foods to reduce blood pressure, describes extra virgin olive oil as the optimal fat choice in the management of hypertension.
Also on the list are foods that often appear alongside extra virgin olive oil on the Mediterranean Diet, including Avocado, Salmon, Almonds and Pumpkin Seeds.
High blood pressure affects millions of people, and finding ways to lower it can be challenging. Fortunately, certain foods can be incredibly beneficial in helping to bring it down. Fruits and vegetables are also key players in the game of lowering blood pressure.
By providing essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, these foods help to relax blood vessels and decrease blood pressure. Another great food to add to your diet is salmon. Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, this fish can help reduce inflammation and lower blood pressure. Finally, nuts are a delicious source of potassium, magnesium, and fiber – all nutrients which can help contribute to a healthy blood pressure range. By incorporating these foods into your diet, you’ll be taking important steps towards lowering your blood pressure and improving your overall health.
Why Diet Can Be As Crucial As Medication For Healthy Blood Pressure
Making smart dietary choices is one effective way to keep high blood pressure in check. One such choice is including extra virgin olive oil in your diet. This oil has been found to have numerous health benefits, including reducing the risk of heart diseases, protecting against inflammation, and potentially even reducing blood pressure. Studies have shown that consuming extra virgin olive oil regularly can help decrease both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
The presence of polyphenols in this oil is believed to be the reason behind its blood pressure-lowering effects, so it’s important to choose extra virgin olive oil over other types to fully reap its benefits. Adding extra virgin olive oil to your dishes not only enhances their flavor but also helps promote a healthy heart.
A recent article from Today points out that diet plays an important role in controlling blood pressure levels and – in some cases – choosing the right diet can be just as effective as medication in controlling blood pressure.
Why Extra Virgin Olive Oil Is One of Top Foods For Blood Pressure Control

The Today article refers to a 2020 study in the journal Nutrients describing olive oil as “ the optimal fat choice in the management protocols for hypertension in both healthy and cardiovascular disease patients.” Olive oil is high in polyphenols and oleic acid, which may help reduce overall risk factors, like blood pressure, for heart disease.
Morocco Gold Extra Virgin Olive Oil And Blood Pressure Control
Thanks to the recent spotlight on the Mediterranean Diet, extensive research has been done on the composition of best olive oil. What has been discovered is an extensive list of phytonutrients; one of the most praised is its polyphenols.
Polyphenols have been shown to reduce morbidity and/or slow down the progression of cardiovascular, neurodegenerative, and cancer diseases. The mechanism of action of polyphenols strongly relates to their antioxidant activity.
Polyphenols are known to decrease the level of reactive oxygen species in the human body. In addition, health-promoting properties of plant polyphenols comprise anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, anti-atherogenic, anti-thrombotic, and anti-mutagenic effects. There is a body of research demonstrating their ability to modulate the human immune system by affecting the proliferation and activity of white blood cells, as well as the production of cytokines or other factors that participate in immunological defence.
Morocco Gold Extra Virgin Olive Oil Is High In Polyphenols
Our latset harvest has produced a low acidity level of 0.2% together with the highest level of polyphenols yet seen in our extra virgin olive oil.
| 3,4 DHPEA-EDA | 85 mg/kg |
| Hydroxytyrosol | 5 mg/kg |
| Lignanes | 26 mg/kg |
| Ligstroside aglycone (p, HPEA-EA) | 20 mg/kg |
| Oleuropein aglycone (3,4 DHPEA-EA) | 71 mg/kg |
| Oleocanthal p, HPEA-EDA | 65 mg/kg |
| Tyrosol | 372 mg/kg |
| Polyphenols Total | 644 mg/kg |
What Other Foods Can Lower Blood Pressure?
If you are looking for a natural way to lower your blood pressure, the good news is that there are plenty of foods, in addition to extra virgin olive oil, that can help you achieve this goal. Among the top 16 foods that can lower blood pressure are leafy greens such as spinach and kale, berries like strawberries and blueberries, beans and lentils, fatty fish like salmon and sardines, whole grains such as oatmeal and brown rice, and fruits like bananas and avocados. By incorporating these foods into your diet, you can work towards reducing your blood pressure and improving your overall health. So, the next time you plan your meals, make sure to add these top 16 foods to your grocery list!
- Avocado
- Beets
- Lemons
- Dark chocolate
- Coffee
- Almonds
- Celery
- Spinach
- Apples
- Wild salmon
- Yogurt
- Pumpkin seeds
- Cinnamon
- Oregano
- Garlic
- Blueberries
All in all, extra virgin olive oil is proving to be one of the best foods to help with lower blood pressure. Not only is it delicious and can add great flavor to many dishes, but also it has a plethora of health benefits that can aid in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
The polyphenols found in extra virgin olive oil are antioxidants that help prevent damage from oxidation and inflammation caused by free radicals, thus reducing the risk for hypertension. It’s important to incorporate healthy cooking oils like extra virgin olive oil into your diet since they provide essential nutrients for sustaining healthy living habits. So next time you shop for ingredients to prepare meals, be sure to pick up some high-quality extra virgin olive oil and benefit from its amazing ability to lower blood pressure!

