Keeping Your Bones Healthy Bones With Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Updated March 11th 2025
Summary
Contents
When it comes to maintaining strong and healthy bones, your diet plays a significant role. While milk and calcium supplements are widely recognized as essential contributors to bone health, there’s another powerful nutrient that deserves attention on this front: extra virgin olive oil (EVOO). Recently, research has uncovered a surprising yet beneficial link between EVOO and bone strength.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil Helps With Bone Strength
Extra virgin olive oil is well-celebrated for its anti-inflammatory properties and cardiovascular benefits, but its impact on bone health is now gaining recognition. EVOO is rich in antioxidants, particularly phenolic compounds, which can help combat oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is a condition that may weaken bones over time, making them fragile and prone to fractures.
Additionally, EVOO encourages calcium absorption, a critical nutrient for strong bones. This capability elevates EVOO as a superfood for not just your heart or skin but also the structure supporting your entire body.
A study published in the journal “PLoS One” found that people who consume The Mediterranean Diet and, in particular olive oil, have denser bones and are less likely to experience bone fractures than those who don’t consume it. Researchers believe that this is due to the anti-inflammatory effects of olive oil, which help keep bones healthy. So if you’re looking for a way to protect your bones, consider adding olive oil to your diet.
The study found:
Overall, our data suggest a protective impact of virgin olive oil as a source of polyphenols in addition to vitamin D3 on bone metabolism through improvement of oxidative stress and inflammation.

Olive oil is loaded with antioxidants and monounsaturated fats, which are essential for bone health. Adding olive oil to your diet can help keep your bones strong and healthy throughout your life. So next time you’re cooking up a storm with some of our recipe inspiration, don’t forget the olive oil!
What is Osteoporosis And How Can Olive Oil Help?
Osteoporosis is a condition where bones become brittle and fragile due to decreased bone density and quality. It is especially common in older adults, particularly women post-menopause, due to hormonal changes that affect bone health. If not addressed, osteoporosis can lead to fractures even from minor falls or bumps.
But how does Extra Virgin Olive Oil play into this? Studies indicate that people following a Mediterranean-style diet, which is high in olive oil, tend to have better bone density than those who don’t. The oleuropein and other polyphenols in olive oil might help stimulate bone-forming cells while reducing bone degradation over time.
By incorporating EVOO into your diet, you could effectively contribute to your daily bone maintenance and potentially slow down the progression of osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis is extremely common, particularly in age groups over 50. There are a number of contributing factors to osteoporosis including ageing, heredity factors, also nutrition and lifestyle. So, how can The Mediterranean Diet, rich in the best extra virgin olive oil help boost your nutritional health?
Skeletal mass and microarchitecture degenerate with aging, thus predisposing the elderly to skeletal fragility and fractures. The global estimate of osteoporotic hip fracture incidence in 2000 was nine million and resulted in more disability adjusted life years lost compared to common cancers excluding lung cancers. The prevalence of osteoporosis is predicted to rise exponentially with the accelerated expansion of elderly population, especially in developing countries. The tremendous economic and healthcare burdens caused by osteoporotic fractures deserve much attention from the medical and scientific community.
Lost bone cannot be replaced, so current treatments focus on preventing the condition from worsening. But did you know that inclusion of a quality extra virgin olive oil in your diet could help to guard against Osteoporosis? According to the Bone Health & Osteoporosis Foundation, the food that you eat can affect your bones. It reminds us that:
Learning about the foods that are rich in calcium, vitamin D and other nutrients that are important for your bone health and overall health with help you make healthier food choices every day. If you eat a well-balanced diet with plenty of dairy, fish, fruits and vegetables, you should get enough of the nutrients you need every day, but if you’re not getting the recommended amount from food alone, you may need to complement your diet by taking multivitamins or supplements.
Studies have shown that a healthy diet like the Mediterranean diet, with extra virgin olive oil as a key constituent leads to decreased fracture incidence.
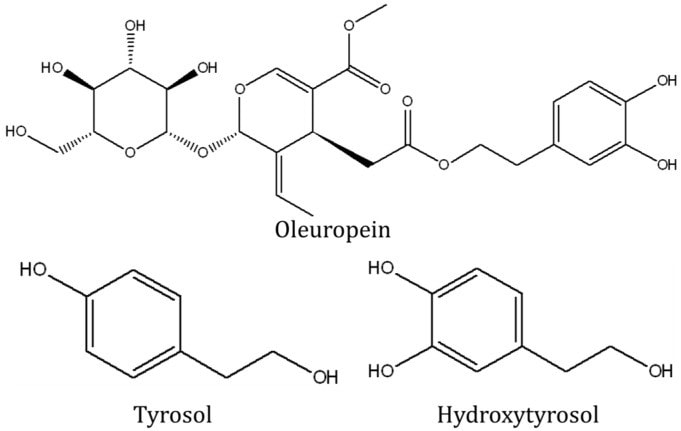
The key polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil that have been shown to reduce risk of bone fracture are Tyroso and Hydroxytyrosol.
Both are present in Morocco Gold extra virgin olive oil.
How Does Extra Virgin Olive Oil Help Keep Bones Healthy

1. It Reduces Oxidative Stress
The antioxidants in EVOO, like vitamin E and polyphenols, help neutralize free radicals that may contribute to bone weakening. Reducing oxidative stress can slow down the deterioration of bone tissue.
2. It Improves Calcium Absorption
Calcium is essential for strong bones, but it needs to be properly absorbed to be effective. Extra virgin olive oil aids in calcium absorption, ensuring your body makes the most of this critical mineral.
3. It Combats Bone Loss
EVOO contains compounds that may interfere with the cells responsible for breaking down bone tissue. By regulating this process, it can help maintain bone density, especially in aging populations.
4. It Supports a Healthy Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet, which is rich in vegetables, nuts, legumes, fish, and, of course, olive oil, has been associated with better overall bone health. EVOO is a staple food in this diet, solidifying its importance for skeletal maintenance.
5. It May Promote Osteoblast Activity Emerging research suggests that some bioactive compounds in EVOO stimulate osteoblasts, the cells responsible for forming new bone. This could be critical in restoring bone density, especially in individuals diagnosed with osteoporosis.
Adherence to a Mediterranean diet with extra virgin olive oil at its heart was associated with decreased fracture incidence in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition Study involving 188,795 subjects followed for nine years. The Mediterranean diet including extra virgin olive oil was also associated with increased calcium absorption and retention and a decrease in urinary calcium excretion in male adolescents.
Olives and extra virgin olive oil are important components in the Mediterranean diet. A Mediterranean diet enriched with olive oil has been associated with increased levels of bone formation markers than non-enriched diet in elderly men.
Mice fed with olive oil also had higher apparent calcium absorption and calcium balance, but a lower serum calcium, phosphate and magnesium level compared to groups fed with other lipids. It is thought that this could be attributed to the high phenolic content of extra virgin olive oil. These phenolic compounds, which include tyrosol, hydroxytyrosol and oleuropein, exert prominent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects; thus are potential candidate agents for osteoporosis prevention.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil & Bone Fractures: A Study
One recent study compared the number of bone fractures in a group of 870 study participants over a period of seven years to see if intake of Extra Virgin Olive Oil was associated with the number of reported bone fractures. When the study results were analysed, the researchers divided this large group into three categories.
In terms of their Extra Virgin Olive Oil intake, the lowest third of the study participants averaged 38 grams of Extra Virgin Olive Oil per day, approximately 3 tablespoons. The middle third averaged nearly 4 tablespoons (48 grams), and the top third averaged about 4.5 tablespoons (57 grams).
Participants in the highest category of Extra Virgin Olive Oil intake reported 51% fewer fractures than participants in the lowest category of Extra Virgin Olive Oil intake.
While all of these Extra Virgin Olive Oil intake levels are fairly high, they nevertheless show a link between reduced risk of bone fracture and incorporation of Extra Virgin Olive Oil into an ordinary meal plan. It’s also worth noting that numerous animal studies have shown increased bone formation in rats and mice that were given Extra Virgin Olive Oil in their feeding plan. This increased bone formation has also been specifically tied to the presence of two phenols, tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol in Extra Virgin Olive Oil.
What Causes Osteoporosis?
Though the exact causes of osteoporosis are unknown, doctors have identified major factors that can lead to the disease.
Aging
Losing bone with age is a natural phenomenon and after the age of 35 the body builds less new bone to replace the loss of old bone. As a general rule, your bone mass goes down as your age goes up, and thus your risk for osteoporosis increases.
Heredity
A family history of the disease, fair skin, and Caucasian or Asian descent can increase the risk for osteoporosis. This fact may help explain why some develop the disease early in life.
Nutrition and Lifestyle
A calcium-deficient diet, excessively low weight, and a sedentary lifestyle have all been linked to osteoporosis, along with smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Medications and Other Illness
Some medications, including steroids, and other diseases like thyroid problems have been linked to osteoporosis.
Treatment
Lost bone cannot be replaced, and as such, treatment focuses on preventing the condition from becoming worse. Treatment plans often involve work from physicians, orthopaedists, a gynecologist, and an endocrinologist. In addition to including regular intake of Extra Virgin Olive Oil, exercise and nutrition as part of your lifestyle choices, other treatments include:
Estrogen Replacement Therapy
- Often offered to women at high risk for osteoporosis, estrogen replacement therapy (ERT) helps prevent bone loss and reduce fracture risk. The hormones also help prevent heart disease and improve cognitive function but can increase the risk for breast cancer.
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators
- Known as SERMs, these anti-estrogens can increase bone mass, reduce fracture risk, and lower the risk for breast cancer.
Calcitonin
- This medication is available in nasal spray form and helps increase bone mass and relieve pain.
Bisphosphonates
- These significantly increase bone mass and help prevent spine and hip fractures.
Conclusion
Olives, extra virgin olive oil or olive polyphenols have the potential to be developed as bone protective agents. This is supported by evidence derived from preclinical studies using animal models of osteoporosis and a limited number of human studies. The bone protective effects of olive and its products are attributed to their ability to increase bone formation and inhibit bone resorption, by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation. However, the exact pathways are still elusive and await future validation. Well-planned randomized controlled trials on olive and its derivatives are warranted to justify its use in osteoporosis prevention.
Anyone experiencing or at risk of the effects of osteoporosis should talk to their doctor to determine the appropriate course of treatment.






