This Valentines Day, Why Extra Virgin Olive Oil Is Your Number One Hero For A Healthy Heart
Updated February 7th 2025

Summary
- As we approach Valentine’s Day, the first thing that comes to mind isn’t usually heart health. However, extra virgin olive oil has a long list of benefits that can help keep your heart healthy and make Valentine’s Day extra special.
- Loaded with health enhancing polyphenols, extra virgin olive oil helps guard your heart against bad cholesterol while promoting good cholesterol.
- Studies have shown that extra-virgin olive oil when used as a regular part of one’s diet can play an effective role in minimizing the risks associated with developing coronary artery disease, stroke, high blood pressure and even diabetes.
- Substituting other fats or oils with extra-virgin olive oil can help you lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases. On top of that, extra virgin olive oil can also aid in weight management and improved digestive health.
- So why not celebrate Valentine’s Day by adding extra virgin olive oil to some of your recipes? By sharing its health benefits with your special someone on Valentine’s Day, you are showing just why extra virgin olive oil is your number one hero for a healthy heart.
Contents
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil In The Mediterranean Diet
- Can Olive Oil Really Reduce Risk Of Heart Disease?
- More Olive Oil Could Help Reduce Your Risk of Heart Disease
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil May Protect Against Stroke
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil is the Best Cooking Oil
- Want To Know More About Links Between Extra Virgin Olive Oil And Heart Health?
Extra Virgin Olive Oil In The Mediterranean Diet
Extra virgin olive Oil has been proven to reduce risk factors associated with heart disease and ldl cholesterol. Therefore, following the Mediterranean Diet is one of the best steps you can take to improve your heart health. By reducing the amount of saturated fats in your diet and replacing it with good sources of Oleic acid – such as a high-quality olive oil – you are taking a significant step towards protecting your heart.
Can Olive Oil Really Reduce Risk Of Heart Disease?
The short answer is Yes – especially if it is high quality extra virgin olive oil.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil (EVOO) is the highest quality olive oil available, extracted from the olive fruit without the use of any heat or chemicals. Regular olive oil is refined and stripped of important nutrients and antioxidants.
In contrast, the natural extraction process used to produce Extra Virgin Olive Oil ensures it retains all the nutrients and antioxidants from the olive fruit.
The fat composition of Extra Virgin Olive Oil is also a major contributor to its healthfulness. It’s primarily made up of monounsaturated fat (approximately 73%), a heart healthy fat that is a staple of the Mediterranean diet.
Studies consistently link a diet high in monounsaturated fat with favourable effects on markers of cardiovascular disease (heart disease and stroke). This includes a reduction in markers of chronic inflammation, blood pressure, cholesterol levels and blood glucose levels.
More Olive Oil Could Help Reduce Your Risk of Heart Disease
Heart disease is the number one cause of premature death worldwide.
Interestingly, populations residing in Mediterranean regions have low rates of mortality (death) from heart disease. While this is due to a combination of factors, their high consumption of Extra Virgin Olive Oil is thought to be a major one.
It appears the active compounds in Extra Virgin Olive Oil have powerful cardio-protective properties, such as helping to lower blood pressure and preventing atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
One giant review study, which included data from over 840,000 subjects, found that those who ate the most olive oil were 9% less likely to have heart issues and 11% less likely to die early compared to those who ate the least olive oil.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil May Protect Against Stroke
Stroke is the second largest killer after heart disease.
It’s closely linked to heart disease and shares many of the same risk factors, such as high cholesterol and high blood pressure.
One French study that compared olive oil use and stroke incidence that those who consumed the highest amounts of olive oil had a 41% lower risk of stroke. A number of other studies have also found similar results.
These findings make sense because people who use olive oil will likely be replacing other less heart healthy fats in their diet. Combine this with the high antioxidant and monounsaturated fat content in Extra Virgin Olive Oil and it’s clear why it appears to have a favourable impact on cardiovascular health.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil is the Best Cooking Oil

There are a lot of different cooking oils that claim to be the best.
However, when you consider the major factors that influence how an oil reacts to high temperatures – oxidative stability and ratio of monounsaturated fats – Extra Virgin Olive Oil is number one.
While virgin coconut oil has a similar oxidative stability (due to its high saturated fat content), it’s extremely low in antioxidants.
Additionally, if you use an oil regularly you must consider the known health effects of its primary fats. Saturated fat (coconut oil) has zero known benefits while monounsaturated fat (olive oil) appears to significantly benefit heart health in the long run.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil is also more practical for cooking because it comes in a variety of different flavour profiles (much like wine) and can complement both sweet and savoury dishes.
Want To Know More About Links Between Extra Virgin Olive Oil And Heart Health?
Most informed websites will point to the health benefits of regularly taking premium quality Extra Virgin Olive Oil like Morocco Gold. We have often discussed these health benefits with our customers at our tasting events. Many of the people we have met wish to know more, so here we are going to provide the science behind what Extra Virgin Olive Oil actually does and why it is good for you. Let’s start by looking at the cardiovascular system
1/ Structures of the Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system is responsible for transporting nutrients and removing gaseous waste from the body. This system is comprised of the heart and the circulatory system. Structures of the cardiovascular system include the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The lymphatic system is also closely associated with the cardiovascular system.
Heart
The heart is the organ that supplies blood and oxygen to all parts of the body. This amazing muscle produces electrical impulses through a process called cardiac conduction. These impulses cause the heart to contract and then relax, producing what is known as a heartbeat. The beating of the heart drives the cardiac cycle which pumps blood to cells and tissues of the body.
Blood Vessels
Blood vessels are intricate networks of hollow tubes that transport blood throughout the entire body. Blood travels from the heart via arteries to smaller arterioles, then to capillaries or sinusoids, to venules, to veins and back to the heart. Through the process of microcirculation, substances such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and wastes are exchanged between the blood and the fluid that surrounds cells.
Blood
Blood delivers nutrients to cells and removes wastes that are produced during cellular processes, such as cellular respiration. Blood is composed of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. Red blood cells contain enormous amounts of a protein called haemoglobin. This iron containing molecule binds oxygen as oxygen molecules enter blood vessels in the lungs and transport them to various parts of the body.
After depositing oxygen to tissue and cells, red blood cells pick up carbon dioxide (CO2) for transportation to the lungs where CO2 is expelled from the body.
Circulatory System
The circulatory system supplies the body’s tissues with oxygen rich blood and important nutrients. In addition to removing gaseous waste (like CO2), the circulatory system also transports blood to organs (such as the liver and kidneys) to remove harmful substances. This system aids in cell to cell communication and homeostasis by transporting hormones and signal messages between the different cells and organ systems of the body. The circulatory system transports blood along pulmonary and systemic circuits. The pulmonary circuit involves the path of circulation between the heart and the lungs. The systemic circuit involves the path of circulation between the heart and the rest of the body. The aorta distributes oxygen rich blood to the various regions of the body.
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is a component of the immune system and works closely with the cardiovascular system. The lymphatic system is a vascular network of tubules and ducts that collect, filter, and return lymph to blood circulation. Lymph is a clear fluid that comes from blood plasma, which exits blood vessels at capillary beds. This fluid becomes the interstitial fluid that bathes tissues and helps to deliver nutrients and oxygen to cells. In addition to returning lymph to circulation, lymphatic structures also filter blood of microorganisms, such as bacteria and viruses. Lymphatic structures also remove cellular debris, cancerous cells, and waste from the blood. Once filtered, the blood is returned to the circulatory system.
2/ Extra Virgin Olive Oil And The Cardiovascular System
Lowering your risk of cardiovascular problems is an area upon which several recent studies on Extra Virgin Olive Oil have focused. Chronic inflammation is a risk factor for many types of cardiovascular disease, and Extra Virgin Olive Oil has well-documented anti-inflammatory properties.
One place we don’t want excessive ongoing inflammation is within our blood vessels. Our blood supply is just too important for maintaining the health of all our body systems, and it cannot effective support our body systems when compromised with ongoing inflammation. Given this relationship, it’s not surprising to see cardiovascular benefits of Extra Virgin Olive Oil rising to the top of the health benefits provided by this remarkable oil.
From a variety of different research perspectives we know that daily intake of Extra Virgin Olive Oil in amounts as low as one tablespoon per day reduces inflammatory processes within our blood vessels. By reducing these processes, Extra Virgin Olive Oil also reduces our risk of inflammation-related cardiovascular diseases like atherosclerosis. Yet anti-inflammatory benefits are not the only cardiovascular benefits provided by Extra Virgin Olive Oil. Two other broad types of heart-related benefits are well documented for this oil. The first type is lessened risk of forming unwanted blood clots. While blood clotting is a natural and healthy process required for the healing of wounds and prevention of excessive bleeding, clotting in the arteries can ultimately result in a heart attack or stroke.
One risk factor for unwanted clotting in our arteries is excessive clumping together of our platelet blood cells. This clumping process is also called “aggregation.” Regular incorporation of Extra Virgin Olive Oil into a meal plan has been shown to lessen the risk of this excessive aggregation, and the reason that researchers refer to Extra Virgin Olive Oil as an “anti-aggregatory” oil.
The other broad area of cardiovascular benefits involves improved levels of circulating fats in our bloodstream, as well as protection of those fats from oxygen-related damage. Decreased levels of total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol following consumption of Extra Virgin Olive Oil are findings are the vast majority of studies that have analysed this relationship.
Yet equally important, the cholesterol molecules that remain in our blood also appear to be better protected from oxygen-related damage (oxidation). Since fats and cholesterol belong to a broader technical category called “lipids,” damage to the fats and cholesterol in our blood stream is typically referred to as “lipid peroxidation.” And it is precisely this lipid peroxidation process that gets reduced through incorporation of Extra Virgin Olive Oil into a meal plan.
3/ Cardiovascular Disease
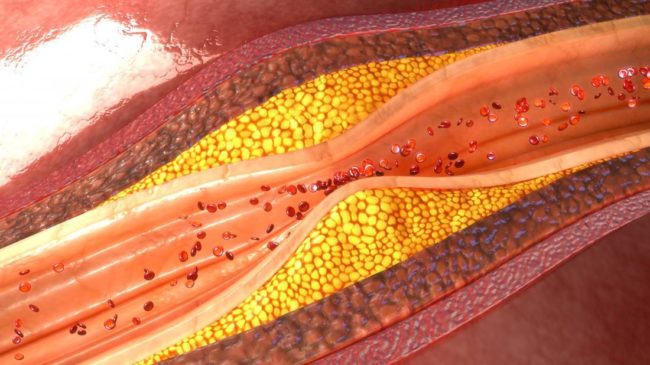
Atherosclerosis is the build-up of fatty plaques on the walls of arteries. Fatty plaque known as atheroma (yellow) has built-up on the inner wall and is blocking about 60% of the artery width. Atherosclerosis leads to irregular blood flow and clot formation, which can block the coronary artery resulting in heart attack.
According to the World Health Organization, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death for people world-wide. Cardiovascular disease involves disorders of the heart and blood vessels, such as coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease (stroke), elevated blood pressure (hypertension), and heart failure.
- Hypertension – persistently elevated blood pressure (high blood pressure) in the arteries. It is associated with the development of disorders such as atherosclerosis, heart attack, stroke, and can cause kidney damage.
- Atherosclerosis – artery walls become hardened due to build-up of plaque (fatty deposits). It causes decreased blood supply to tissues and may lead to blood clots, stroke, aneurysm, or heart disease.
- Aneurysm – a bulging in a weakened area of an artery that could rupture and cause internal bleeding.
- Coronary artery disease (heart disease) – narrowing or blockage in the coronary arteries, which supply blood directly to the heart muscle. Complete blockage of blood flow will cause a heart attack.
- Stroke – death of brain cells (neurons) due to lack of blood supply.
- Heart failure – the heart is not able to supply enough blood to body tissues. It is caused by conditions such as hypertension, heart disease, and cardiomyopathy (chronic disease of the heart muscle).
It is crucial that the organs and tissues of the body receive proper blood supply. Lack of oxygen means death, therefore having a healthy cardiovascular system is vital for life. In most cases, cardiovascular disease can be prevented or greatly diminished through behavioural modifications. Individuals wishing to improve cardiovascular health should consume a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and abstain from smoking.
Imagine your body as a highly complex, high-performance engine. High quality Extra Virgin Olive Oil like Morocco Gold is natures highest performance engine oil, to keep your body well- tuned and running smoothly over a lifetime.
