New Research Shows Avocado and Extra Virgin Olive Oil Boost Heart Health
Updated March 20th 2024

Summary
- Avocado Oil And Extra Virgin Olive Oil are two of the stand-out healthy fats and they have lots in common but some differences in health benefits.
- Both Avocados and Extra Virgin Olive Oil are a rich source of monounsaturated fats.
- Avocados contain lutein and zeaxanthin, antioxidants that are beneficial for eye health where olive oil contains antioxidants such as vitamin E and polyphenols which help neutralize free radicals.
- Nutritionists and Chefs recommend both avocado and extra virgin olive oils as they each have unique flavours and considerable health benefits.
Contents
- Considering Which Is Better For Health: Extra Virgin Olive Oil Or Avocado Oil.
- Health Benefits of Avocado Oil
- What Do The Experts Say About Extra Virgin Olive Oil Or Avocado Oil?
- Health Benefits of Extra Virgin Olive Oil
- Choosing The Right Fat To Combat Heart Disease
- Monounsaturated Fats Support A Healthy Diet
- How to Avoid Excess Weight Gain And Maintain A Healthy Diet
- What Is In 1 Tablespoon Of Extra Virgin Olive Oil?
- Conclusion: Extra virgin olive oil and Avocado Oil both have many health benefits.
Considering Which Is Better For Health: Extra Virgin Olive Oil Or Avocado Oil.
In recent years, avocados and extra virgin olive oil have taken center stage in the world of healthy eating. These two food items have become popular not just as ingredients in delicious recipes but also as superfoods with significant health benefits.
But what makes them stand out as “healthy fats,” and why should food enthusiasts and health-conscious individuals consider incorporating them into their diet?
Eating at least two servings of avocado a week reduced the risk of having a heart attack by 21% says a new study this week. But lovers of olive oil don’t have to change their healthy fat as olive oil and avocado are great together!
According to the latest research from the Journal of the American Heart Association, eating avocados reduced the risk of heart attacks in both men and women, including when eaten in place of butter, cheese or processed meats.
“Although no one food is the solution to routinely eating a healthy diet, this study is evidence that avocados have possible health benefits,” said Cheryl Anderson, chair of the American Heart Association’s Council on Epidemiology and Prevention, in a statement. Anderson was not involved in the study.
“We desperately need strategies to improve intake of AHA-recommended healthy diets — such as the Mediterranean diet — that are rich in vegetables and fruits,” said Anderson, who is also professor and dean of the Herbert Wertheim School of Public Health and Human Longevity Science at University of California San Diego.
Health Benefits of Avocado Oil:
Avocados are rich in monounsaturated fats, particularly oleic acid, which is known for its positive impact on heart health. Unlike saturated fats, which can raise the body’s levels of bad cholesterol, monounsaturated fats help maintain good cholesterol levels and reduce inflammation, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Heart Health: The “good” fats in avocado can help lower bad cholesterol levels and support heart health.
- Nutrient Absorption: They enhance the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like vitamins A, D, E, and K.
- Fiber Content: High fiber content contributes to weight management and digestive health.
- Antioxidants: Avocados contain lutein and zeaxanthin, antioxidants that are beneficial for eye health.
What Do The Experts Say About Extra Virgin Olive Oil Or Avocado Oil?
If, as Anderson suggests, you choose to align your lifestyle with the Mediterranean diet, to reduce your ldl cholesterol levels replacing saturated fats with foods containing monounsaturated fatty acids is vital. Both avocado and olive oil have a very similar fatty acid composition, containing over 70 percent monounsaturated fatty acids. Both foods have been shown to reduce inflammation and protect against heart disease.
According to a recent article in Healthline.com both Avocado Oil and Olive Oil have been proven to reduce levels of ldl cholesterol – the bad kind and protect against heart disease. Healthline reports:
Both avocado oil and olive oil are primarily made up of oleic acid, a beneficial monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid. Studies have shown that foods rich in oleic acid may benefit your health. Particularly, they may help reduce inflammation and blood pressure levels.
Healthline.com
When it comes to choosing the best olive oil for oleic acid, the principles are simple. There are different grades of olive oil according to its level of acidity, or level of free oleic acid within the olive oil. The amount of free oleic acid in olive oil indicates the extent to which fat has broken down into fatty acids. To qualify as extra virgin olive oil, it is an olive oil of less than 0.8% acidity and has no taste defects. In practice, the very best extra virgin olive oils have acidity levels much lower. Morocco Gold extra virgin olive oil is consistently below 0.5%, normally around 0.25% to 0.3% depending on the weather conditions throughout the growing season.
Health Benefits of Extra Virgin Olive Oil:
Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) is another excellent source of monounsaturated fats, primarily oleic acid. It is a staple in the Mediterranean diet, which has been associated with a multitude of health benefits.
- Cardiovascular Benefits: EVOO can improve heart health by regulating cholesterol levels and preventing inflammation.
- Rich in Antioxidants: It contains antioxidants such as vitamin E and polyphenols which help neutralize free radicals.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: The compound oleocanthal in EVOO has been found to have anti-inflammatory effects similar to ibuprofen.
- Cancer Prevention: Some studies suggest that the antioxidants in EVOO may help protect against certain types of cancer.
Choosing The Right Fat To Combat Heart Disease

Dietary fats are an essential part of a healthy diet according to the American Heart Association. Firstly, the right fats provide energy, improve cell growth and absorption of nutrients, and create important hormones. Not only does extra virgin olive oil like Morocco Gold consist mainly of healthy monounsaturated fats. Secondly, this fat that contains high levels of polyphenols. The antioxidants associated with a range of health benefits. However, this makes extra virgin olive oil without question the healthiest of all fats and an essential part of a healthy diet.
Fats consist of fatty acids and glycerol. A fatty acid is a chain of carbon atoms. Each carbon atom in the chain is attached to hydrogen atoms. The number of hydrogen atoms per carbon atom determines whether the fatty acid is saturated or unsaturated. Therefore will contribute towards a healthy diet.
Saturated fats
Firstly, if a fatty acid has all of the hydrogen atoms it can hold (2 per carbon atom in the chain) and all of the carbon atoms in the chain are linked by single bonds, it is described as saturated.
Secondly, saturated fats are usually solid or semi-solid at room temperature. Nutritionists recommend eating them as little as possible. Lard, butter, hard cheeses, whole milk, animal fats and palm and coconut oils. They can cause high blood pressure. Plus products containing them – all contain high levels of saturated fat that do not support a healthy diet.
Monounsaturated Fats Support A Healthy Diet
There is a common misconception that fats cause weight gain, making some people wary of foods like avocados and olive oil. However, healthy fats are actually crucial for weight management as they provide a sense of satiety that can curb overeating. Both avocado and extra virgin olive oil can be part of a healthy diet when used in moderation.
A pair of carbon atoms in the fatty acid chain linked by a double bond instead of a single bond is described as a monounsaturated fat. Monounsaturated fat tends to be liquid at room temperature. Olive oil is one of the richest sources of monounsaturated fatty acids and therefore supports a healthy diet.
Monounsaturated fats—omega-6s in the case of olive oil—are important because they help boost heart health. This is important for helping prevent health issues such as cardiovascular disease or stroke.
Polyunsaturated fats
These contain more than one double bond and are liquid at room temperature. The main sources are vegetable oils, such as sunflower oil, corn oil and rapeseed, but not tropical oils such as coconut, palm and palm kernel oils.
Trans fats
Trans fats are created when a hydrogenation process is applied to solidify oil for use in margarines or to improve a product’s shelf life. This processing causes trans fats to act like saturated fats.
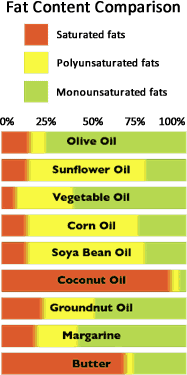
The following illustrates the differing fat contents of a range of products.
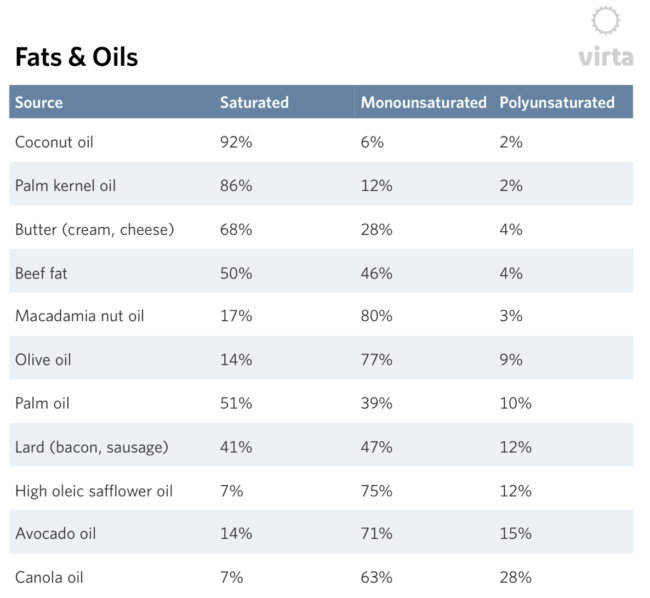
What Is In 1 Tablespoon Of Extra Virgin Olive Oil?
One serving or 1 tablespoon of extra-virgin olive oil contains the following:
- 120 calories
- 10 grams of monounsaturated fat
- 2 grams of saturated fat
- 2 grams of polyunsaturated fat
- 1.9 milligrams of vitamin E (10 percent of Daily Value)
- 8.1 micrograms of vitamin K (10 percent of DV)
Not All Calories Are Created Equal
As part of maintaining a healthy diet many people want to know how many calories are in olive oil. Research has shown that not all calories are necessarily equal.
In a famous study at Middlesex Hospital in London in the 1950s, two British researchers, Professor Alan Kekwick and Dr. Gaston L.S. Pawan, tested a series of diets on overweight patients. The patients on a high-carbohydrate diet consistently gained or sustained weight, even when given limited calories. Conversely, subjects on a high-fat diet lost considerably more weight than any of the other diets, even when provided with excess calories.
A more recent study published in The Journal of the American Medical Association also challenges the notion that a “calorie is just a calorie.” Led by Cara Ebbeling, PhD, associate director and David Ludwig, MD, director of the New Balance Foundation Obesity Prevention Center at Boston Children’s Hospital, the purpose of the study was to learn what kind of diet helped people maintain their new weight after successfully losing weight. The results indicated that a low-fat diet predicts weight regain, while diets featuring a moderate to high percentage of calories from fat both increased subjects’ energy expenditure and reduced the surge in their blood sugar after eating, making these diets preferable to a low-fat diet for those trying to achieve lasting weight loss.
How to Avoid Excess Weight Gain And Maintain A Healthy Diet
Adding extra virgin olive oil to your healthy diet provides your body with important nutrients and all the healthy fats it needs. This reducing the cravings that lead to nutrient-empty foods like soft drinks, cookies and breads.
Extra virgin olive oil reduces the risk of acid reflex and prevents gastric juices from traveling back up from the stomach to the esophagus. Olive oil inhibits gastric acid’s motility (the ability to move food through the digestive tract). Because of this, the stomach’s gastric content releases more gradually and slowly into the duodenum, making one feel fuller and benefiting from full nutrient absorption in the intestine. By emphasizing nutrient-rich extra virgin olive oil alongside vegetables and protein in your healthy diet, you can avoid excess consumption of weight-inducing sugars and grains.
By feeding your body the healthy fats it needs and increasing your intake of olive oil, research shows you will feel more full for a longer period of time and be less tempted to overeat, making extra virgin olive oil an important aid in weight loss and improved health for adults and children alike.
On the other hand, consumption of man-made trans fats found in hydrogenated and refined vegetable oils interferes with numerous biochemical processes in the body and can cause serious health problems and contribute to weight gain. Using extra virgin olive oil as part of a healthy diet can instead begin reversing the negative effects of trans fats.
Conclusion: Extra virgin olive oil and Avocado Oil both have many health benefits.
Avocado and extra virgin olive oil are considered healthy fats because they contribute to heart health, combat inflammation, and are rich in antioxidants, among other benefits. As part of a balanced diet, they can be powerful allies in maintaining your well-being. Not only that, their potential in various dishes makes them essential items in any health-conscious foodie’s pantry.
Next time you’re at the grocery store, remember that the fats found in avocados and extra virgin olive oil are nothing to shy away from. Grab that vibrant green fruit or that bottle of golden oil and give your meals—and your health—a boost.
Whether you’re an aspiring chef exploring new recipes or someone just starting your health and wellness journey, consider avocados and extra virgin olive oil your trusted companions. They remind us that not all fats are created equal, and when chosen wisely, they can significantly elevate both the flavor of our food and the quality of our health.
