Which Diet Incorporates The Benefits Of Olive Oil Better?
Updated 1st May 2023

When attempting to live a healthier lifestyle, olive oil has been hailed as nature’s superfood because of its many health benefits.
Contents:
- The Health Benefits Of The Mediterranean Diet and the Vegan Diet
- How Olive Oil is Used in the Mediterranean and Vegan Diets
- Both diets rely heavily on fresh fruit and vegetables which are packed with antioxidants
- A Healthy Diet Includes Extra Virgin Olive Oil
- Study Into Extra Virgin Olive Oil As Part Of A Healthy Diet
- Can a diet rich in Extra Virgin Olive Oil improve your Cardiovascular Health?
- What Are Polyphenols?
- What Makes Morocco Gold Extra Virgin Olive Oil So Special?
- Types Of Polyphenols
- Morocco Gold Extra Virgin Olive Oil Is High In Polyphenols
- What Conditions Can Extra Virgin Olive Help To Alleviate?
The Health Benefits of The Mediterranean Diet and The Vegan Diet
Deciding the best way to consume this culinary staple can be confusing; two popular and often contradicting diets that focus on consuming extra virgin olive oil are the Vegan diet and Mediterranean diet. Both have distinct advantages when it comes to utilizing the full spectrum of health benefits of extra virgin olive oil – but which one should you choose? In this blog post, we’ll explore each in more detail and assess their individual pros and cons when it comes down to reaping all-important heart-healthy gains from incorporating olives into your daily dietary routine. So let’s dig in!
How Olive Oil is Used in the Mediterranean and Vegan Diets
Olive oil is a staple ingredient in Mediterranean and vegan diets, and for good reason. Not only is it a delicious and versatile cooking oil that can be used in a variety of dishes, but it is also a key component of these healthy, plant-based diets. In the Mediterranean diet, which is celebrated for its many health benefits, olive oil is a primary source of healthy fats and is consumed in abundance alongside other nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, and fish.
Meanwhile, in vegan diets, olive oil serves as a plant-based alternative to butter or other animal fats and is used for everything from sautéing vegetables to dressing salads. Whether you’re following a Mediterranean diet or a vegan one, incorporating olive oil into your cooking is an easy and delicious way to boost your health and support your dietary goals.
A fascinating new report from LiveScience has compared the relative health benefits of the Mediterranean Diet and the Vegan Diet – both hugely popular as plant based nutritional choices.
The Mediterranean Diet And Cardiovascular Health
When it comes to healthy eating, there are two popular diets that tend to get a lot of attention: the Mediterranean Diet and the Vegan Diet. Both of these diets have been shown to offer numerous health benefits and they both encourage the use of healthy fats like extra virgin olive oil, but which one is the best for you?
According to a new report from LiveScience, both have potential benefits for health, as well as a lot of scientific research backing them up as nutritious options for most people. But there are some key differences that are worth looking out for, especially if you have certain health conditions or dietary requirements.
The Mediterranean Diet is based on the traditional foods that are consumed in countries like Greece, Italy, and Spain. The diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, fish, and olive oil. This diet has been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and obesity.
“Both diets are fairly different, and I wouldn’t say one is better than the other one,” says Roxana Ehsani, registered dietitian nutritionist and national media spokesperson for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. “If followed correctly, both can be nutritious diets.”
“The vegan diet is becoming more popular, it’s a diet which eliminates all animal products and dairy products like cheese or yogurt or eggs, and strictly consuming plant-based foods,” says Ehsani. “You are able to eat vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, soy foods like tofu, plant-based milk options like almond milk, grains, seeds, legumes like beans and lentils.”
The Vegan Diet is a plant-based diet that excludes all animal products, including meat, dairy, and eggs. This diet has been shown to lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Additionally, both the Vegan and Mediterranean Diet has been linked with a reduced risk of developing certain types of cancer.
Both diets rely heavily on fresh fruit and vegetables which are packed with antioxidants
Speaking to LiveScience, Ehsani said:
The Mediterranean diet is another great option for cardiovascular health, according to Ehsani. “The Mediterranean diet is a heart healthy diet, and has been extensively studied and rated by the U.S. News & World Report as typically the best diet overall when it comes to following a healthy eating plan,” she says. “The Mediterranean diet consists of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, monounsaturated fats such as olive oil, lean meats, seafood, legumes and nuts.
So, which diet is the best for you? Ultimately, the choice depends on your own personal preferences and lifestyle. But the great news for lovers of extra virgin olive oil is that it is a key ingredient in both diets.

A Healthy Diet Includes Extra Virgin Olive Oil
For those who are tempted by the recent swell in popularity of plant-based, Keto or Mediterranean diets, did you know that the best olive oil you can afford is an essential component of them all?
Rich in disease fighting antioxidants called Polyphenols, Extra Virgin Olive Oil is a versatile and delicious ingredient in many plant-based, Mediterranean, and Keto recipes. Polyphenols decommission a nasty molecule in your body called free radicals. Free radicals can ricochet around inside your body and harm good cells. Antioxidants, such as the polyphenols found in Extra Virgin Olive Oil, work to neutralize free radicals, protecting the body from their harmful antics.
A flavoursome alternative to vegetable oil, extra virgin olive oil such as Morocco Gold can be used both to cook with, as a dip or to drizzle over your favourite salads.
Many of us are turning to plant-based or vegan diets for weight loss, environmental reasons, and other personal choices.
Debate over which diet is best overall for cardiovascular health continues to rage among nutritionists, scientists and consumers.
Study Into Extra Virgin Olive Oil As Part Of A Healthy Diet
A recent study in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition that found a low-fat vegan diet leads to greater weight loss, healthier cholesterol levels and increased insulin sensitivity compared with the Mediterranean diet.
For 16 weeks, researchers from the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine had one-half of study participants go on a low-fat vegan diet focused on fruits, vegetables, whole grains and legumes. The other half went on the Med diet, focusing on fruits, vegetables, legumes, fish, low-fat dairy and extra-virgin olive oil — while limiting red meat and saturated fats. Both groups then went back to their ordinary way of eating for four weeks before switching to the opposite diet for another 16 weeks.
Participants lost an average of 13 pounds on the vegan diet (improving insulin resistance) — but nothing on the Mediterranean one. However, those on the Mediterranean Diet reported a significant benefit to systolic blood pressure — it declined by 9.3 mmHg; only 3.4 on the vegan diet. This is good news for your heart in a number of ways.
According to Harvard Health Publishing, the Mediterranean diet has been shown in both large population studies and randomized clinical trials to reduce risk of heart disease, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, certain cancers (specifically colon, breast, and prostate cancer), depression and, in older adults, a decreased risk of frailty, along with better mental and physical function.
Can a diet rich in Extra Virgin Olive Oil improve your Cardiovascular Health?
Lowering your risk of cardiovascular problems is an area upon which several recent studies on Extra Virgin Olive Oil have focused. Chronic inflammation is a risk factor for many types of cardiovascular disease, and Extra Virgin Olive Oil has well-documented anti-inflammatory properties.
One place we don’t want excessive ongoing inflammation is within our blood vessels. Our blood supply is just too important for maintaining the health of all our body systems, and it cannot effective support our body systems when compromised with ongoing inflammation. Given this relationship, it’s not surprising to see cardiovascular benefits of Extra Virgin Olive Oil rising to the top of the health benefits provided by this remarkable oil.
Yet anti-inflammatory benefits are not the only cardiovascular benefits provided by Extra Virgin Olive Oil. Two other broad types of heart-related benefits are well documented for this oil. The first type is lessened risk of forming unwanted blood clots. While blood clotting is a natural and healthy process required for the healing of wounds and prevention of excessive bleeding, clotting in the arteries can ultimately result in a heart attack or stroke.
One risk factor for unwanted clotting in our arteries is excessive clumping together of our platelet blood cells. This clumping process is also called “aggregation.” Regular incorporation of Extra Virgin Olive Oil into a meal plan has been shown to lessen the risk of this excessive aggregation, and the reason that researchers refer to Extra Virgin Olive Oil as an “anti-aggregatory” oil.
The other broad area of cardiovascular benefits involves improved levels of circulating fats in our bloodstream, as well as protection of those fats from oxygen-related damage. Decreased levels of total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol following consumption of Extra Virgin Olive Oil are findings are the vast majority of studies that have analysed this relationship.
Yet equally important, the cholesterol molecules that remain in our blood also appear to be better protected from oxygen-related damage (oxidation). Since fats and cholesterol belong to a broader technical category called “lipids,” damage to the fats and cholesterol in our blood stream is typically referred to as “lipid peroxidation.” And it is precisely this lipid peroxidation process that gets reduced through incorporation of Extra Virgin Olive Oil into a meal plan.
It is crucial that the organs and tissues of the body receive proper blood supply. Lack of oxygen means death, therefore having a healthy cardiovascular system is vital for life. In most cases, cardiovascular disease can be prevented or greatly diminished through behavioural modifications. Individuals wishing to improve cardiovascular health should consume a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and abstain from smoking.
Imagine your body as a highly complex, high-performance engine. High quality Extra Virgin Olive Oil like Morocco Gold is nature’s highest performance engine oil, to keep your body well- tuned and running smoothly over a lifetime.
What Are Polyphenols?
Polyphenols are a group of over 500 phytochemicals, which are naturally occurring micronutrients in plants. These compounds give a plant its colour and can help to protect it from various dangers. When you eat plants with polyphenols, you reap the health benefits as well.
They also protect the olive oil from oxidative damage and contribute to its superior longevity and shelf life. They also affect the taste of extra virgin olive oil and give it its distinctive bitter flavour.
What Makes Morocco Gold Extra Virgin Olive Oil So Special?
The high polyphenol content of Morocco Gold extra virgin olive oil is dependent on three factors. First is the variety of the olive, secondly the climate and terroire of the growing region and thirdly the actual time in the growing season that the crop is harvested.
Morocco Gold is pressed from the Picholine Marocaine, the only type of olive to go into Morocco Gold. Oil from this variety is renowned for it’s high polyphenol count, oxidative stability and longevity.

Our olives are grown in a valley that is about 2,000 feet above sea level. This helps to create the additional climatic challenges that encourage polyphenol uptake within the olive tree. It is also an area with naturally occurring high phenols in the soil itself.
In soils, phenols are released over extended period of time from decomposing plant materials. This causes complex organic compounds to be slowly oxidized or to break down into simpler forms of sugars, amino sugars, aliphatic and phenolic organic acids. These are further transformed into microbial biomass or are reorganized, and further oxidized, into humic assemblages (fulvic and humic acids), which bind to clay minerals.
There has been a long debate about the ability of plants to uptake humic substances through their root systems and to metabolize them. There is now a consensus about how humus plays a hormonal role rather than simply a nutritional role in plant physiology. Olive trees grown in ‘challenging’ conditions encourage the uptake of naturally occurring phenols in the soil. This in turn aids the circulatory system within the olive tree, with the phenols eventually finding their way to the olive fruit itself.
Thirdly, our olives are picked when the fruit is young and green. As the olives age on the tree, the colour of the olive changes to red and then black, the size of the olive increases thus producing more oil, but the polyphenol level decreases. There is a great deal of expertise within the farming community where we source our oil to ensure that the harvest is collected at the optimum time to maximise the polyphenol level.
Types Of Polyphenols
There are a number of different types of polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil, including oleuropein, tyrosol, hydroxytyrosol, oleocanthal and oleacein. Each are considered extremely strong antioxidants, and are linked to a number of different health benefits.
Morocco Gold Extra Virgin Olive Oil Is High In Polyphenols
Our latest harvest has produced a low acidity level of 0.2% together with the highest level of polyphenols yet seen in our extra virgin olive oil.
| 3,4 DHPEA-EDA | 85 mg/kg |
| Hydroxytyrosol | 5 mg/kg |
| Lignanes | 26 mg/kg |
| Ligstroside aglycone (p, HPEA-EA) | 20 mg/kg |
| Oleuropein aglycone (3,4 DHPEA-EA) | 71 mg/kg |
| Oleocanthal p, HPEA-EDA | 65 mg/kg |
| Tyrosol | 372 mg/kg |
| Polyphenols Total | 644 mg/kg |
What Conditions Can Extra Virgin Olive Help To Alleviate?
The following illustrates the range of chronic conditions where research into these polyphenols oil has demonstrated positive effects.
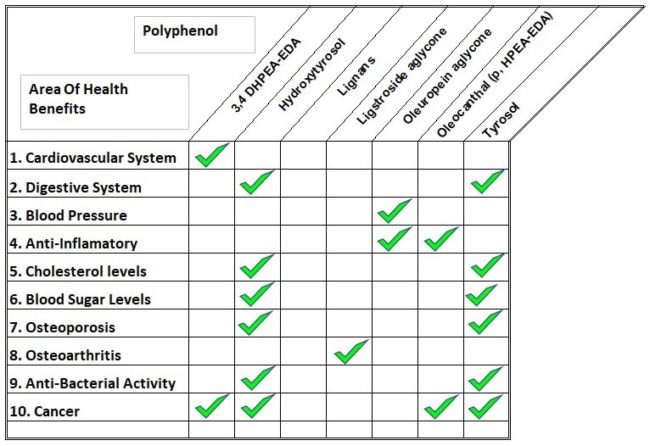
In fact the European Food Safety Authority has now approved health claims for extra virgin olive oils with polyphenol content of more than 250mg / kg. Morocco Gold contains polyphenols well above this level.
