And shows how the best olive oil – extra virgin olive oil – contributes to loosing weight with Mediterranean diet.
Updated February 16th 2023

Summary:
- A new study shows that the Mediterranean diet can reduce abdominal fat
- Including extra virgin olive oil being the best olive oil for the Mediterranean diet contributes significantly to weight loss.
- Eating foods rich in monounsaturated fatty acids such as are found in extra virgin olive oil will help reduce your belly fat storage.
- So if losing extra abdominal fat has been on your mind, it’s time to stock up on extra virgin olive oil and experience its amazing effects as part of your Mediterranean diet.
Contents:
- Study links Mediterranean Diet With Abdominal Weightloss
- A Healthy Mediterranean Diet For Weightloss
- Why Are Healthy Fats Good For Weight Loss?
- The Mediterranean Diet and Pregnancy
- 3 Tablespoons Of Extra Virgin Olive Oil Can Help To Make You Slimmer
- Veg And Extra Virgin Olive Oil: A Perfect Match
- Want To Maintain A Healthy Weight? Here’s What You Need To Know About Fats
Study links Mediterranean Diet With Abdominal Weightloss
Following a Mediterranean Diet is listed as one of five key ways to reduce abdominal fat, according to a new report in Eat this, Not that.
Finding a healthy diet for weightloss is a constant challenge for many of us. In particular, finding effective ways to reduce abdominal fat is often a key priority – especially as we approach the warmer months when our summer wardrobes are being considered.
The high dependency on monounsaturated fatty acids in the Mediterranean Diet is credited with helping to reduce ‘belly fat storage’ says the report. According to Rasa Kazlauskaite, MD, and Sheila Dugan, MD; “The popular ‘flat belly diets’ embrace much of the wisdom found in eating a Mediterranean diet, which helps everything from brain health to heart health. The basic premise for both diets is to eat foods rich in monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) that may help reduce your belly fat storage. MUFA-rich foods include olive oil, nuts and seeds, avocados, and fish. Eating yogurt regularly has also been found to be helpful in reducing belly fat.”
Unsurprisingly, the other lifestyle choices listed in the report are: getting enough exercise and sleep, quitting smoking and taking time to ‘chill out’.
A Healthy Mediterranean Diet For Weightloss
An ever-rising bank of evidence suggests that following a Mediterranean Diet, including healthy fats such as extra virgin olive oil can contribute to maintenance of a healthy weight and reduce obesity.
There have been many studies over recent times that support this claim. Research showing that men who were overweight or obese who replaced saturated fat with monounsaturated fats in their diets experienced small but significant weight loss, compared with a saturated-fat-rich diet, despite no major change in total fat or calorie intake.
As reported in Healthline, more recent research states that unsaturated fatty acids are likely to be more beneficial than saturated fats when it comes to healthy weight maintenance.
Clinical trials on animals have also revealed strong evidence to show that replacing a high fat diet with a high monosaturated fats have been known to prevent weight gain.
Healthline also explains that extra virgin olive oil is a rich source of medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which have been studied for their ability to play a role in healthy weight loss and maintenance.
Why Are Healthy Fats Good For Weight Loss?

While it would be understandable to assume that all fats contribute to weight gain, researchers Shatha Hammand and Peter Jones recently stated that “[u]nsaturated FA, polyunsaturated FA (PUFA) and monounsaturated FA (MUFA), have been found to suppress appetite as well as increase energy expenditure and fat oxidation rate. This, therefore, results in favourable effects on total fat mass.”
Olive oil and extra virgin olive oil is full of monounsaturated fatty acids. Along with keeping your heart healthy and blood sugar levels in check, these fats promote the feeling of being full. This, in turn, means you are less likely to binge on other less healthy, refined or trans-fat food sources with a high calorific content.
And the benefit to enjoying a Mediterranean diet as part of maintaining a healthy weight starts before we are even born.
The Mediterranean Diet and Pregnancy
A recent study, published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition suggests that the children of mothers who eat a diet rich in inflammatory foods including sugars, artificial trans fats and processed meats will experience greater weight gain between the ages of three and ten years.
The findings of this latest research add weight to previous understanding that weight gain problems may begin in pregnancy as pathways that program metabolism and patterns of eating are sensitive to in utero influences.
Among the recommendations from the research team is that pregnant women consider a Mediterranean Diet, high in plant-based foods, including extra virgin olive oil, fish and unsaturated fats to benefit both mother and child’s health. These foods provide important sources of vitamin D, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, and other nutrients that have been shown to be beneficial for offspring health.
In their study, Author Carmen Monthé-Drèze and colleagues analysed data on 1,459 mother-child pairs collected by Project Viva — an ongoing study into maternal and child health being conducted at the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute in Massachusetts.
During their respective pregnancies, each mother was asked to complete questionnaires on their dietary intake, which the researchers interpreted through the lens of three different dietary indices. These included the Dietary Inflammatory Index, the Mediterranean diet score, and the Alternate Healthy Eating Index for Pregnancy.
After giving birth, each child was weighed and measured several times between birth and adolescence, from which body mass index (BMI) values were calculated. Finally, the researchers analysed how each mother’s dietary index scores were associated with their offspring’s growth trajectory.
“Maternal nutrition during pregnancy may have a long-term impact on children’s weight trajectories,” said Dr Monthé-Drèze. She added that the findings suggest “there are specific developmental periods when nutrition during pregnancy may influence offspring growth. We found that a pregnancy diet with higher inflammatory potential was associated with faster BMI growth rates in children between three and ten years of age.” She added “We also found that lower adherence to a Mediterranean-style diet during pregnancy was associated with higher BMI trajectories through adolescence.”
Researchers also revealed that, of those taking part in the study, mothers who more closely followed an anti-inflammatory diet including extra virgin olive oil, were also more likely to be well-educated, have a higher income, and less likely to smoke or have obesity themselves. As reported in Insider, this is likely due to the fact that financial and social resources impact dietary health and consistent access to healthy food makes a difference in preventing obesity.
3 Tablespoons Of Extra Virgin Olive Oil Can Help To Make You Slimmer
Extra Virgin Olive Oil is great for drizzling over salads and creating that perfect bruschetta. It is, unquestionably the most flavor-some and aromatic of all the olive oils. It is also incredibly healthy. Extra Virgin Olive Oil has been widely researched and the health benefits are evidence based including:
- Reduced of risk of cardiovascular diseases
- Beneficial effect on ulcers and gastritis
- Maintains the digestive tract in good health
- Helps to reduce blood pressure
- Help control healthy cholesterol levels
- Olive oil eases or prevents diabetes
- Olive oil lessens the severity of osteoporosis
It has now been shown to have proven weight-loss properties, which can be achieved by having three tablespoons or about 50ml of extra virgin olive oil a day.
These are the findings of US nutritionist and associate professor of clinical medicine Dr Mary Flynn, who’s been studying the effects and health benefits of extra virgin olive oil since the 1990s.
“The general body of research says that once you have two or more tablespoons a day, you’ll improve your blood pressure, your glucose levels and your good cholesterol,” Flynn says. “But I’ve found that the weight-loss effect comes into play at three tablespoons, so that’s what I recommend. It’s an amazing food – it does all these things that help your body, plus it tastes good.”
It’s important to note that when Flynn refers about “olive oil”, she’s talking about extra-virgin olive oil, like Morocco Gold which is rich in nutrients.
Consuming three tablespoons of extra virgin olive oil isn’t enough to start shedding the kilos, Flynn says, explaining that the weight-loss effect kicks in when it’s combined with a healthy Mediterranean-style diet. This is rich in vegetables, fruit, legumes and whole grains, moderate in dairy and low in meat (about three serves of white meat or fish a week for women, and red meat only once or twice a month).
“This way of eating essentially takes the calories you’d normally be consuming with meat and gives them to vegetables and extra virgin olive oil,” she says.
Flynn proved the success of a diet that’s high in healthy fats in 2010 with a study of 44 women over 50 who’d become overweight during breast cancer treatment. Each woman trialled two eight-week diets: Flynn’s extra virgin olive oil-based diet and a low-fat food plan as recommended by the US National Cancer Institute. Both diets were made up of 1500 calories a day.
After the 16 weeks, the average weight loss was 7kg, however, the women lost twice as much on the extra virgin olive oil diet as the low-fat diet, and they also showed improved breast cancer biomarkers, lower triglycerides and higher levels of the “good” HDL cholesterol. In addition, when the women were asked to choose the diet they preferred, all but one chose the olive oil diet as they found the food more appetising, accessible and affordable.
While the benefits of being a healthy weight are particularly important to women who’ve had breast cancer (being overweight increases the risk of the cancer recurring), being overweight or obese also increases the risk of cancer and other illnesses generally. “I recommend this diet to everyone,” Flynn says
Veg And Extra Virgin Olive Oil: A Perfect Match
Flynn says the key to the success of the extra virgin olive oil diet is to cook your vegetables in olive oil. There are two main reasons for this. The first is that carotenoids – the powerful antioxidants that give orange, yellow and red veg their colour and are also found in abundance in leafy greens – need fat to be absorbed. She also believes the nutrients in cruciferous veg such as broccoli and cabbage are better absorbed with oil, but that’s still yet to be conclusively proven. The second reason is arguably more important: Vegies taste better with extra virgin olive oil, so people are likely to eat more.
“My rule of thumb is one tablespoon of extra-virgin olive oil to one cup of veg,” Flynn says, adding that sautéing them or roasting are tasty options, plus these methods maintain much of their nutrient value. “Eating veg like this fills you up and stops you being hungry.” An added bonus, she says, is fibre from the veg also improves bowel regularity.
For anyone daunted by a diet of less meat and three cups daily of vegetables, Flynn advises: “Start by having three dinners a week where you combine vegetables, extra virgin olive oil and some starch (potatoes or wholegrain pasta or rice). Then see if you can add some lunches in as well. The more you take in, the more benefit you’ll get.”
Want To Maintain A Healthy Weight? Here’s What You Need To Know About Fats

According to sports dietitians Kelly Jones, M.S., R.D. and Lori Nedescu, M.S., R.D.N. extra virgin olive oil is one of the healthiest oils because of its heart-healthy fats.
Source: https://www.bicycling.com/health-nutrition/a27240925/is-olive-oil-health
Fat is a nutrient with important functions. It is a rich source of energy, providing more than double that of either carbohydrate or protein. It is a carrier for the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K. It provides the essential fatty acids, linoleic and alpha-linolenic acid, which are polyunsaturated.
To remain healthy, we need moderate amounts of the right type of fats eaten as part of a good, balanced diet. However, a high fat intake and in particular, a high intake of saturated fats is associated with raised blood cholesterol and coronary heart disease.
Not All Fats are the Same
Fats are made up of fatty acids and glycerol. A fatty acid consists of a chain of carbon atoms, where each carbon atom in the chain is attached to hydrogen atoms. The number of hydrogen atoms per carbon atom determines whether the fatty acid is saturated or unsaturated.
Saturated Fats
If a fatty acid has all of the hydrogen atoms it can hold (2 per carbon atom in the chain) and all of the carbon atoms in the chain are linked by single bonds, it is described as saturated.
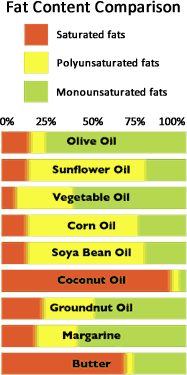
They are usually solid or semi-solid at room temperature and are strongly associated with raised blood cholesterol which is why nutritionists recommend eating them as little as possible. Lard, butter, hard cheeses, whole milk, animal fats and palm and coconut oils – plus products containing them – all contain high levels of saturated fat.
Monounsaturated Fats
If a pair of carbon atoms in the fatty acid chain is linked by a double bond instead of a single bond, the fatty acid is described as monounsaturated. Fats rich in monounsaturates tend to be liquid at room temperature. Olive Oil is one of the richest sources of monounsaturated fatty acids.
Monounsaturated fats—omega-6s in the case of olive oil—are important because they help boost heart health. This is important for helping prevent health issues such as cardiovascular disease or stroke.
Polyunsaturated Fats
These contain more than one double bond and are liquid at room temperature. The main sources are vegetable oils, such as sunflower oil, corn oil and rapeseed, but not tropical oils such as coconut, palm and palm kernel oils.
Trans Fats
Trans fats are created when a hydrogenation process is applied to solidify oil for use in margarines or to improve a product’s shelf life. This processing it to act like a saturated fats.
What Is In 1 Tablespoon Of Extra Virgin Olive Oil?
One serving or 1 tablespoon of extra-virgin olive oil contains the following:
- 120 calories
- 10 grams of monounsaturated fat
- 2 grams of saturated fat
- 2 grams of polyunsaturated fat
- 1.9 milligrams of vitamin E (10 percent of Daily Value)
- 8.1 micrograms of vitamin K (10 percent of DV)
The following illustrates the differing fat contents of a range of products.