Why We Should Choose Foods With A High Polyphenol Content?
Updated February 23rd 2025

Summary
- Leading Gastroenterologist says polyphenol rich foods like extra virgin olive oil are good for your health.
- Quality extra virgin olive oil has the highest polyphenol content.
- Studies show polyphenols have major health benefits including supporting cardiovascular health, brain health, managing weight and reducing inflammation.
Contents
- Leading Gastroenterologist Says Polyphenols Are Important For Gut Health
- How Can Polyphenol Rich Olive Oil Benefit Your Health?
- How to get polyphenols in your diet from Olive Oil And Other Sources
- The Polyphenols Present In Morocco Gold Extra Virgin Olive Oil
- Polyphenol Sources Including The Best Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Gastroenterologist Says Polyphenols In Olive Oil Are Important For Gut Health
If you’re keen to explore what the nutrients in the food you eat can do for your gut health, it might be a good idea to explore the wonders of polyphenols. In this post, we’ll explain why a leading Gastroenterologist believes that polyphenols are so important for gut health – and how you can make sure to get enough of them in your diet. Polyphenols are a type of phytonutrient found in plant foods, including extra virgin olive oil, that have antioxidant properties.
In fact the European Food Safety Authority has now approved health claims for extra virgin olive oils with polyphenol content of more than 250mg / kg. Morocco Gold olive oil has high polyphenols well above this level.
They’ve been shown to be beneficial for gut health in multiple ways, including by inhibiting bad bacteria, encouraging the growth of good bacteria, and protecting the gut lining. But don’t take it from us, listen to the words of an expert!
How Can Polyphenol Rich Olive Oil Benefit Your Health?
In the increasingly health-conscious world we live in today, gut health has become not just a topic of interest but a significant concern for many. From health enthusiasts to nutritionists, the quest for the optimal diet that supports a healthy digestive system is ongoing.
Among the various compounds studied for their beneficial effects on our bodies, polyphenols have recently garnered attention, especially from gastroenterologists. But why? What makes these compounds so special, and how do they contribute to gut health?
How to Incorporate Polyphenols into Your Diet
The good news is that it’s relatively easy to increase your intake of polyphenols. Here are some tips:
- Eat a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables: Aim for a rainbow on your plate to ensure you’re getting a wide range of polyphenols.
- Savor your tea and coffee: Both beverages are rich in polyphenols, just be mindful of the caffeine content.
- Don’t forget about nuts and seeds: These are not only great sources of healthy fats but also polyphenols.
Enjoy dark chocolate in moderation: Dark chocolate is not only delicious but also packed with polyphenols. Just make sure it’s high in cocoa content and low in sugar.
Writing in MindBodyGreen.com, Integrative Gastroenterologist Marvin Singh, M.D. says he is always looking for the best foods and nutrients that can help my patients live their healthiest lives. And this has led him to the door of polyphenols. Pointing out that many of us may be aware of the potential benefits of drinking green tea or adding olive oil to the diet and eating plenty of vegetables but questions if we really know why?
Did you know that part of the reason for these recommendations has to do with compounds called polyphenols? Polyphenols are found in lots of plant-based foods and have been found to have numerous benefits for health.
Research has revealed numerous potential benefits of polyphenols, many of which have to do with reducing the risk of chronic disease or even supporting gut health.
Marvin Singh, M.D
He goes on to list what he calls the most ‘noteworthy perks’ or health benefits of polyphenols:
1. Boost mitochondrial health.
Mitochondria are the powerhouses inside our cells, generating most of the energy we need to function. Over time, oxidative stress and age contribute to the decline in mitochondrial function, and our health suffers as a result. Several studies have shown that polyphenols and their metabolites, like Urolithin A, can help repair and rejuvenate mitochondria.
2. Protect against pathogens.
Polyphenols also have antimicrobial properties, meaning they can help protect the gut from various pathogens. By inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria and fungi, these compounds can reduce the risk of infections and support the body’s natural defense mechanisms.
The polyphenols found in green and black tea have been shown to inhibit the growth of different bacteria and viruses such as hepatitis C virus, influenza virus, E. coli, and Salmonella. There is ongoing research on how polyphenols might influence gut health and potentially promote beneficial bacteria, which helps support a strong immune system, as well.
3. Promote cardiovascular health.
Studies have shown that intake of polyphenols from foods like tea, nuts, cocoa, grapes, and legumes may reduce the risk of heart attack, as well as help control cholesterol levels and blood pressure.
4. Promote brain health.
Consuming polyphenols from chocolate and green and black tea on a regular basis has been shown to reduce the risk of brain function decline over time. One study also showed potential benefits for the brain of infants, when mothers consumed polyphenol-rich pomegranate juice.
5. Help to manage weight.
Studies suggest that the polyphenols in items such as green tea, grapes, and turmeric may help support a healthy weight.
6. Gut support.
Polyphenols’ health benefits also come from what happens in our gut when we eat foods containing them. One example is Urolithin A (UA), a compound that is produced in the gut when we eat polyphenols from foods like berries, nuts, and pomegranates.
How to get polyphenols in your diet from Olive Oil And Other Sources
As Dr Singh perfectly summarise, the single most effective way to increase your polyphenol intake is certainly to consume a variety of plant-source foods. At Morocco Gold, we are delighted to see that a quality extra virgin olive oil (such as our own) takes its place on his list!
- Olive oil. Extra-virgin olive oil has been shown to have the highest level of polyphenols.
- Spices and dried herbs. Try cloves, star anise, peppermint, and Mexican oregano.
- Red wine. Red wine contains several types of polyphenols, including resveratrol.
- Black and green tea. These beverages are rich in several types of polyphenols, like catechins.
- Coffee. The antioxidant polyphenols (caffeine, chlorogenic acid, diterpenes, and trigonelline) in coffee have been shown to support brain health.
- Cocoa powder and chocolate. Rich in several types of polyphenols, mainly catechins and proanthocyanidins.
- Fruits. Berries (especially dark ones) and pomegranates are a particularly good source of polyphenols, in particular anthocyanins and ellagitannins.
- Vegetables. Black and green olives, globe artichoke heads, red and green chicory, onion, shallot, and spinach are good sources.
- Grains. Whole grain flours from wheat or rye have several different types of polyphenols.
- Nuts and seeds. Flaxseed is rich in lignans, whereas others like chestnut and walnut, hazelnut, pecan nut, and almond contain other types.
Polyphenols are found in a wide variety of plant-source foods. These range from fruits and vegetables to herbs and spices to grains and more. A plant-based diet should generally be rich in various types of polyphenols.
The Polyphenols Present In Morocco Gold Extra Virgin Olive Oil

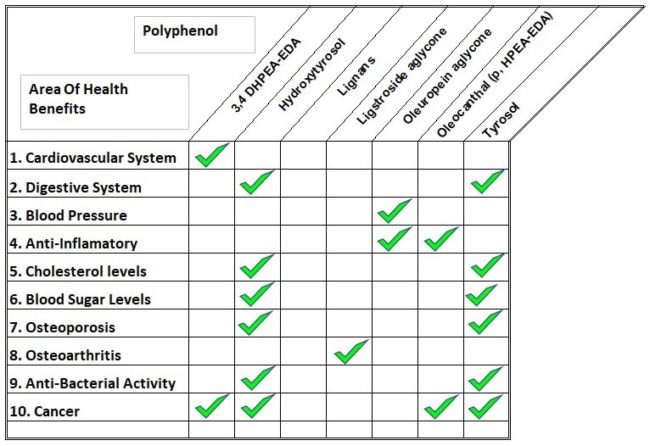
We are delighted to say the total polyphenol count in our latest harvest of Morocco Gold extra virgin olive oil is:
| 3,4 DHPEA-EDA | 85 mg/kg |
| Hydroxytyrosol | 5 mg/kg |
| Lignanes | 26 mg/kg |
| Ligstroside aglycone (p, HPEA-EA) | 20 mg/kg |
| Oleuropein aglycone (3,4 DHPEA-EA) | 71 mg/kg |
| p, HPEA-EDA | 65 mg/kg |
| Tyrosol | 372 mg/kg |
| Polyphenols Total | 644 mg/kg |
Polyphenol content in Morocco Gold Extra Virgin Olive Oil
The following illustrates the range of chronic conditions where research into these polyphenols oil has demonstrated positive effects.
Polyphenol Sources Including The Best Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Polyphenol rich olive oil is receiving the attention of scientific and health community lately because of their benefits for human body. Polyphenols are chemical compounds that are present in many natural foods. Polyphenol is also used as dietary supplements and can be taken as prescribed medicine.
Polyphenols are phytochemicals that occur in plants and render the colour to plants. Sources of polyphenols include peaches, pomegranate, grapes, oranges, cocoa powder and dark chocolate. However one of the most important sources of polyphenols is extra virgin olive oil. It is important that this is genuine, unprocessed extra virgin olive oil like Morocco Gold that will still have its polyphenols intact. Processed or refined olive oils usually have their polyphenols extracted from the oil during filtration and refining.
Research has shown that polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil have a massive and positive impact on health and doctors recommend high consumption of polyphenol sources. Health benefits of high polyphenol extra virgin olive oil include:
Polyphenols In Extra Virgin Olive Oil Act As An Antioxidant
The polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil act as an antioxidant which means that these compounds minimize free radicals in the body. Antioxidants affect the human health in various way from improving body functions and digestion to skincare. Antioxidants can also fight off cell damage in the body, enhancing the body’s capability to fight off any diseases.
Polyphenols Rich Olive Oil Lowers Cholesterol
Polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil can help you to maintain a healthy cholesterol level. There is good cholesterol, and bad cholesterol in the body and higher level of bad cholesterol increases the risk of heart diseases, choking arteries. Therefore, the polyphenols in the extra virgin olive oil can help you maintain cholesterol level within safe limits.
Extra Virgin Olive Oil Improves Artery Function
The inner surface of the blood vessels and lymphatic vessels are made from endothelial cells. According to the studies, polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil have a direct impact on the growth of the endothelial cell, regulating the functions of the blood vessel. Along with this, there is a positive impact of polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil on genes expression which regulates angiogenesis and other roles of the endothelium.
As extra virgin olive oil in itself has antioxidant characteristics, the high polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil can improve the overall endothelium resulting in improved cardiovascular health.
Polyphenols In Extra Virgin Olive Oil Prevents Platelet Clumping Within Arteries
Platelet clumping is a type of a human health problem which is also called platelet aggregation. In platelet clumping, the platelets clump or coagulate together, and it can lead to the formation of clots in the blood. The polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil inhibit platelet clumping in blood, preventing the formation of harmful or unnecessary blood clots. In case of bruise or bleeding, the platelet clump together to form a clot to stop bleeding. But a high aggregation level may lead to the development of blood clots in the body.
Use In Extra Virgin Olive Oil Fight Inflammation
Polyphenol rich olive oil fights inflammation in the body and can regulate muscle damage or chemicals that cause inflammation. As inflammation is related to various other diseases, polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil help to fight these diseases including cardiovascular problems.

